Last Updated on August 22, 2025 by Muhamed Elmesery
In fluid mechanics, Archimedes principle is one of the most critical principles with several applications in our daily life. The principle was established by Archimedes, a Greek mathematician, when he tried to determine the authenticity of a golden crown commissioned by Hiero II. He reportedly ran out of the tub and rushed home naked, shouting!! ”Eureka” (which means I have found it in Greek).
In this blog post, we will understand what is Archimedes principle, and answer the top questions about it.
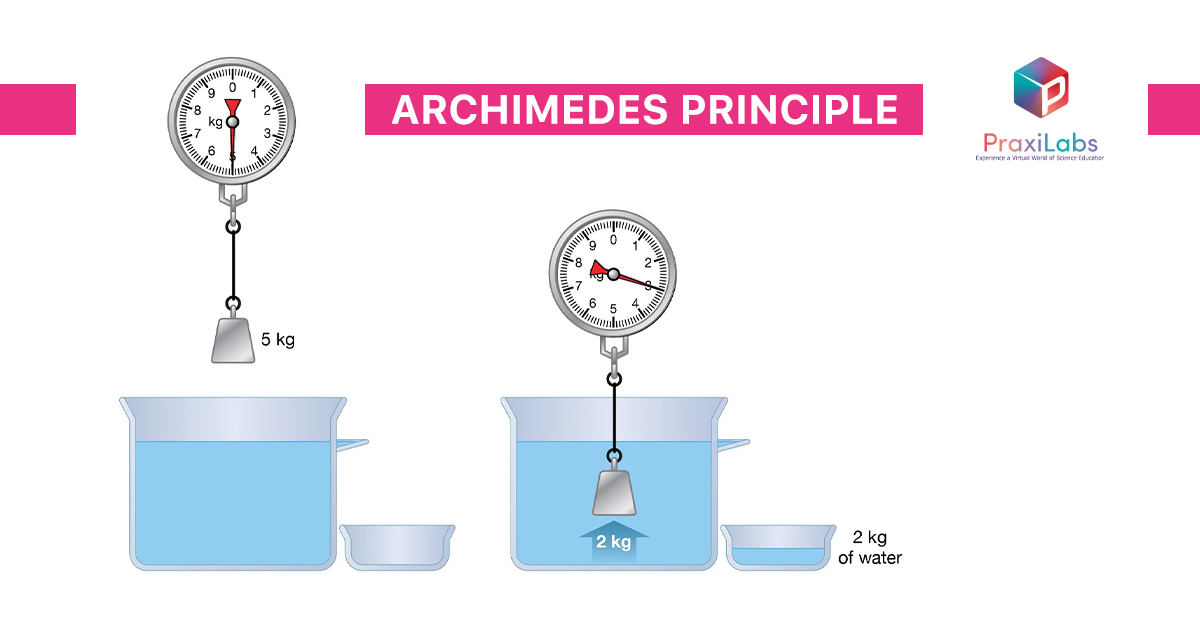
Table of Contents
What is Archimedes Principle?
Archimedes principle states that “the upward buoyant force that is exerted on a body immersed in a fluid, whether wholly or partly submerged, is equal to the weight of the fluid that the body displaces and acts in the upward direction at the center of the mass of the displaced fluid”.
In other words, Archimedes’ principle proves that if a body is immersed in a liquid, it will be acted upon by upward force (Buoyant force) equal to the weight of the displaced liquid.
Archimedes’ principle is a consequence of Newton’s third law the weight of the object equals the weight of displaced liquid in equilibrium (floating).
Archimedes’ principle is an idealization. Surface tension, pressure asymmetry, the nature of the solvent and other factors cause it to break down for complex liquids.
One of the most critical importance of Archimedes’ Principle is that explains why ships made of heavy materials can still float? Even though materials like steel are heavier than water, ships can float because of their design, it allows them to displace a large volume of water, resulting in a buoyant force that counteracts their weight.
How did Archimedes formulate his principle?
When Archimedes tried to reveal the authenticity of a golden crown commissioned by Hiero II:
- He took one mass of silver and another one of gold, both equal in weight to the crown.
- He filled a container to the brim with water, then put the silver in and noticed how much water the silver pushed out.
- He refilled the container again and put the gold in, and noticed how much water the gold pushed out.
- He found that the gold displaced less water than the silver.
- He then put the crown in the same container and found that it pushed out more water than the gold and indicating that the crown was mixed with silver.
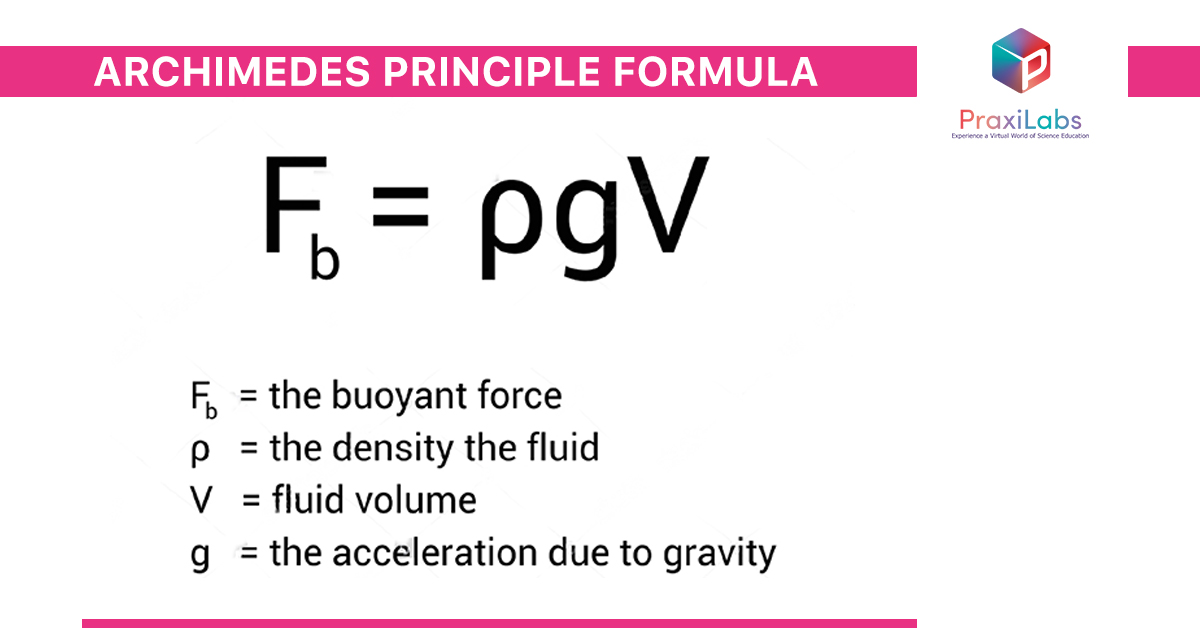
Equation of Archimedes Principle
The equation of Archimedes principle is given by the following formula:
Where:
- g is the acceleration due to gravity.
- p a density of pushed out fluid.
- V is the volume of pushed out fluid.
Buoyant force Fb is depends on some factors:
- Volume of the displaced fluid.
- Volume of the body submerged in liquid.
- Density of the displaced fluid.
- Acceleration due to gravity.
How do you study Archimedes principle in the laboratory?
We can study Archimedes principle in the laboratory by following these steps:
- Take a beaker filled with water to the brim.
- Measure the weight of any solid body using a spring balance and record it.
- Keep the body attached to the spring balance, then immerse it in the water.
- Just make sure the spring balance is not submerged.
- Record the weight shown by the spring balance.
- Note that the last weight is less and some water will be pushed out.
- Collect the displaced water and weigh it.
- Now, you will find that the weight of the pushed out water is equal to the loss of weight of the body.
From the previous experiment, we can prove Archimedes principle, which states that “When a body is completely or partially immersed in a fluid (liquid or gas),it is acted upon by an upward force called “Upthrust or buoyant” that is equal to the weight of the displaced fluid by the body. Also, the volume of the immersed body equals the volume of the displaced fluid ”
How can you prove that Archimedes principle is experimentally?
You can prove that Archimedes principle experimentally by applying the following steps:
- Take a metal object and determine whether it is made of aluminum, brass, copper, or iron (steel).
- Record the material on your data sheet.
- Measure and record the mass of your metal object.
- Measure and record the mass of the wood block.
- Temporarily remove the pan from the balance. Raise the shelf to its highest position. Replace the pan. Check that your balance is still zeroed.
- Fill a beaker about ¾ full of water and place it on the shelf.
- Attach a string to the metal object and suspend it from one of the hooks where the pan attaches to the balance.
- Adjust the amount of water in the beaker and/or the length of the string so that the metal object is completely submerged in the water, but not touching the sides or bottom of the beaker.
- Measure and record the balance reading.
- Remove the metal object and replace it with the wooden block and the metal sinker, with only the metal sinker completely submerged. Measure and record the balance reading.
- Make sure neither object is touching the beaker.
- Repeat the previous step with both the sinker and the wooden block completely submerged.
- Empty the beaker and put the lab equipment away. Wipe up any water on the balance or lab table.
Source: Archimedes’ principle. Available at: https://collegeofsanmateo.edu/physics/docs/physics210/lab11.pdf (Accessed: 26 June 2024).
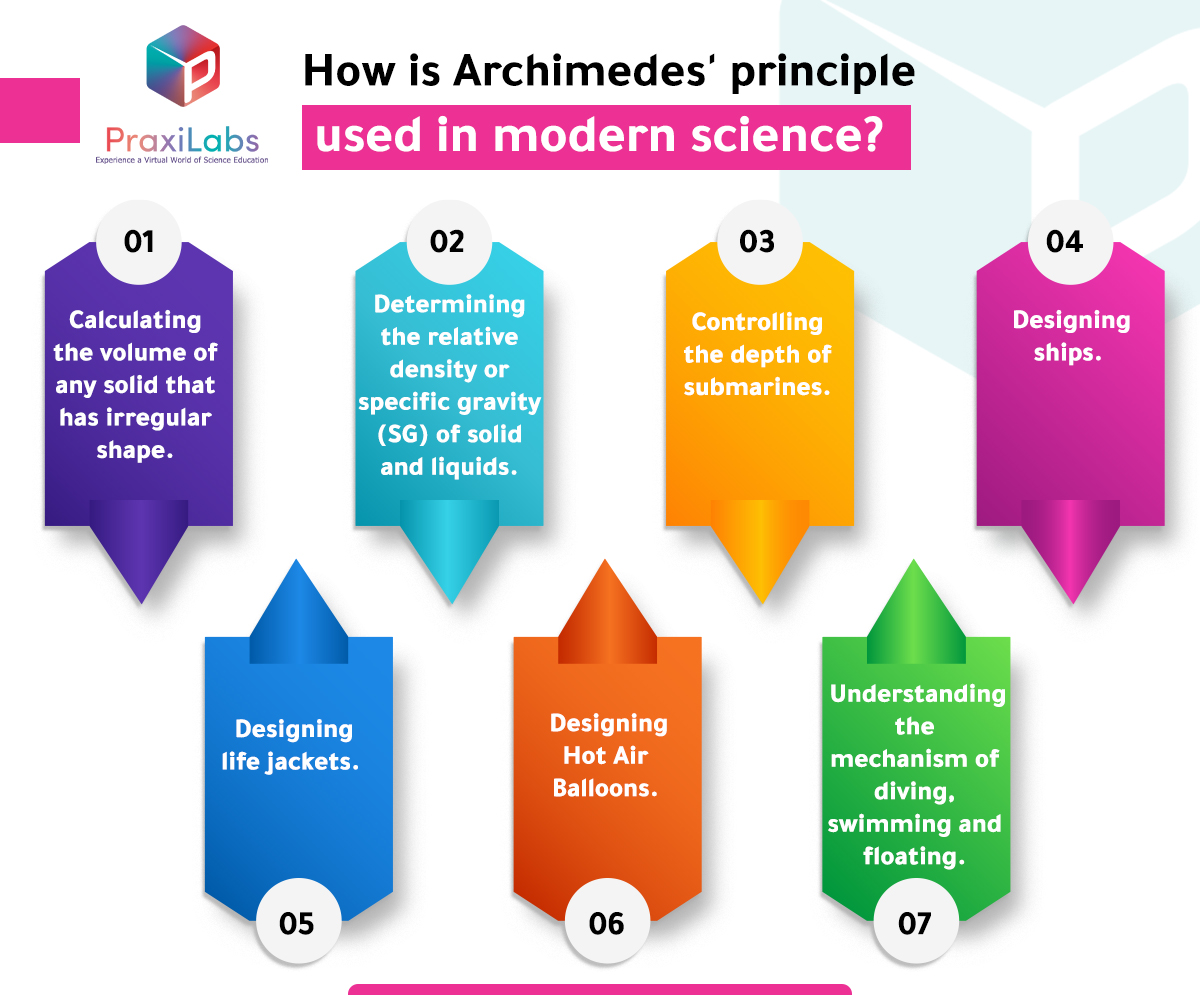
How is Archimedes principle used in modern science?
There are several applications and uses of Archimedes principle in modern science such as:
- Calculating the volume of any solid that has irregular shape.
- Determining the relative density or specific gravity (SG) of solid and liquids.
- Controlling the depth of submarines.
- Designing ships.
- Designing life jackets.
- Designing Hot Air Balloons.
- Understanding the mechanism of diving, swimming and floating.
Explore Archimedes Principle Virtual Laboratory in Science Education
Virtual laboratories simulations play a vital role in science education, as they enrich the experimentation process through visual aids that guide the students through the process. Students no longer get stuck but rather enjoy the help of a virtual laboratory partner when needed, while also receiving guidance to prevent wrong choices. Moreover, students are quickly tested on the basic results of their experiments to ensure an enhanced learning experience.
On PraxiLabs, we provide our students with smart realistic 3D science experiments simulations.
Archimedes principle simulation from PraxiLabs aims to determine the specific gravity of a solid “ρs” and the specific gravity of a liquid “ρL”.
By weighing a body in air, water and a liquid, we can detect the specific gravity of the body and the liquid through simple relations that are based on Archimedes’ principle.
By the end of the experiment, students can:
- Understand and explain Archimedes’ principle.
- Apply Archimedes’ principle to a body that is completely immersed in water and other liquids.
- Set up an experiment to determine the specific gravity of both a solid and a liquid.
By applying the following procedures, you will perform the Archimedes principle simulation from PraxiLabs successfully:
- From the drop-down list, choose one liquid (other than water) to determine its specific gravity.
- The mass of the body m in air is shown on the balance screen.
- Click the Record button to record this value.
- Immerse the body inside the beaker full of water and find the mass of the body mw.
- Click the Switch Liquids button to bring the beaker with the liquid beneath the body.
- Immerse the body inside the beaker full of the liquid.
- Click the Record button to record this value mL .
- The experiment is complete, and an Excel sheet that contains the recorded data will be downloaded.
Our physics virtual simulations are characterized by the following features:
- Impressive Design & Enhanced User Experience
- Immediate Feedback
- Bilingual and ready for more
- Adaptive to Learning Styles
- LMS Integration
- Additional Content
- Cost Effective & Affordable
- Anywhere, Anytime
- Immersive interaction and 3D simulation
- Safety.
Discover Physics Like Never Before: Access PraxiLabs Virtual Physics Labs Instantly!
PraxiLabs virtual labs provide students and educational organizations with a large catalog of virtual experiment simulations for college students. Without the hazards or high costs, students can learn and understand scientific concepts and techniques through our physics virtual lab.
We provide virtual labs for physics experiments in several sub-disciplines such as:
- Properties of matter virtual labs.
- Waves virtual labs.
- Modern physics virtual labs.
- Heat and thermodynamics virtual labs.
- Mechanics virtual labs.
- Magnetism virtual labs.
- Electricity virtual labs.
Are you tired of seeing your students struggle to grasp complex scientific concepts? With PraxiLabs’ virtual labs, your students will no longer get stuck in traditional learning methods. By incorporating virtual simulations into your curriculum, you can significantly increase their learning retention and engagement.
Increase your Students’ Learning Retention and Engagement!
 PraxiLabs A virtual world of science
PraxiLabs A virtual world of science






