Last Updated on October 19, 2025 by Muhamed Elmesery
To understand and study the world of microorganisms, we need special techniques or methods that are called “Microbiology techniques”. Microbiology techniques are the methods used for studying microbes (ex: bacteria, fungi and protest). The purpose of these techniques include microbial identification, staining, engineering, survey, culturing and manipulation.
Table of Contents
What are Microbiological Techniques?
Microbiology lab techniques refers to the set of procedures used to study and examine the characteristics of microbes for many scientific purposes.
The most common microbiology lab techniques are:
- Aseptic techniques.
- Staining techniques.
- Culturing techniques.
- Isolation techniques.
- Differentiation techniques.
Microbiological Techniques examples
Now we will mention some of microbiological techniques examples:
1. Microbiology Aseptic Techniques
The main importance of aseptic techniques in microbiology is creating suitable controlled conditions to prevent or at least reduce the contamination from other microbes (that entering unsterile sources like water or air or dust) as much as possible so we can grow and study specific microorganisms.

Examples of microbiology aseptic techniques used in laboratories:
-
Sterilization
Sterilization is used to remove all other forms of microbial organisms like bacteria, viruses, fungus, spores, and other vegetative cells from the culture or the surface of the media.
To destroy and kill the unwanted forms of microorganisms and contaminants, sterilization techniques depend on using:
- Filtration – heat – drying – radiations like UV and gamma radiation (physical methods)
- Chemicals like alcohol – phenols – detergents – dyes (chemical methods).
-
Sanitization
This method depends on the complete elimination of all microbes (pathogenic or non-pathogenic) from the surface top to reduce contamination and prevent infections as much as possible. It’s commonly used in our daily lives to sanitize our hands.
Sanitization involves the use of chemical cleaners like alcohol-based cleaners, formaldehyde, chlorine-based cleaners and hydrogen peroxide.
-
Culturing Techniques
Culturing is one of the primary microbiology techniques that is used in the process of isolating microbes caused infectious diseases in labs. The culturing is done to support the growth of specific pathogens. The pathogen is grown on culture media which is necessary for providing the nutritional requirements.
Types of Culture Media
There are 3 main types of culture media used for testing pathogens:
- Solid culture media: It consists of a mixture of nutrients, agar and salts with a solid surface. This type is used mainly for bacteria and fungi culturing. The single cultured microbe can then grow into colonies which contain thousands of cells.
- Liquid culture media: In this type the microbial cells are grown inside a liquid media and translate it to a colloidal suspension. From determining the time taken for the liquid media to form the colloidal suspension we can detect the microbial growth. This type is used mainly for detecting parasites and mycobacteria.
- Cell culture media: Animal or human cell cultures are infected with the wanted microbe. Then, these cultures are observed to detect the microbial effect on the cells. This type is used mainly for identifying viruses.
Note: Before introducing the microbial strain to the culture media, the inoculation and isolation techniques are done.
Inoculation is one of microbiology techniques used to place microbial strains onto culture media by using an inoculation loop.
Isolation is one of microbiology techniques used to isolate a specific microbial strain from a mixed microorganisms culture by culturing the wanted microbes on a selective culture media.
Culture media can also classified (depending on their components) into:
- Simple media: It mainly consists of (sodium chloride+ peptone+ meat extracts+ water) ex: the nutrient broth.
- Complex media: This type of media, it contains other special ingredient in addition to the previous components to enhance a special characteristic and provide nutrients for the growth of certain types of microbes. It may contain extracts from animals, plants or yeast, such as yeast extracts, blood, milk, serum, milk, meat extracts, peptone and soybean digests.
- Synthetic media: It’s used mainly for research purposes. They are prepared by:
-following an exact formula.
-Mixing a certain amounts of organic and inorganic chemicals and with distilled water.
- Special media: This type of media supports the isolation and growth of special condition and type of bacteria and this is difference than what happened at the basic simple media which a broad spectrum microbial growth.
3. Staining Techniques in Microbiology
Staining is one of microbiology techniques that used to examine and define the different forms of microbes or the cell cycle stages or the cell organelles like mitochondria in microscopic scale.
Staining techniques in microbiology depend on dying or coloring the cells and other structures to be highlighted for viewing often with the aid of microscopes.
Top types of Staining Techniques in Microbiology
-
Simple Staining
Simple staining depends on using only single dye like methylene blue and crystal violet which are used to determine the shape, size and arrangement of the cells.
The steps are:
1- Apply a single dye to a fixed smear in order to color the microorganisms.
2- Cover the fixed smear with stain and wait for a specific period.
3- Then, wash off the solution with water and dry the slide.
-
Differential Staining
This type of staining technique is used to differentiate microorganisms based on the properties of staining. More than one dye is used to distinguish organisms. For example: gram staining, acid-fast staining, endospore staining, and metachromatic staining.
Gram Staining
It is one of the most important and widely used differential staining techniques in microbiology. It is called gram staining after the Physician Christian Gram introduced it in 1884 and it is used to divide bacteria into two categories (Gram positive and Gram negative).
The following figure illustrates Gram staining procedure
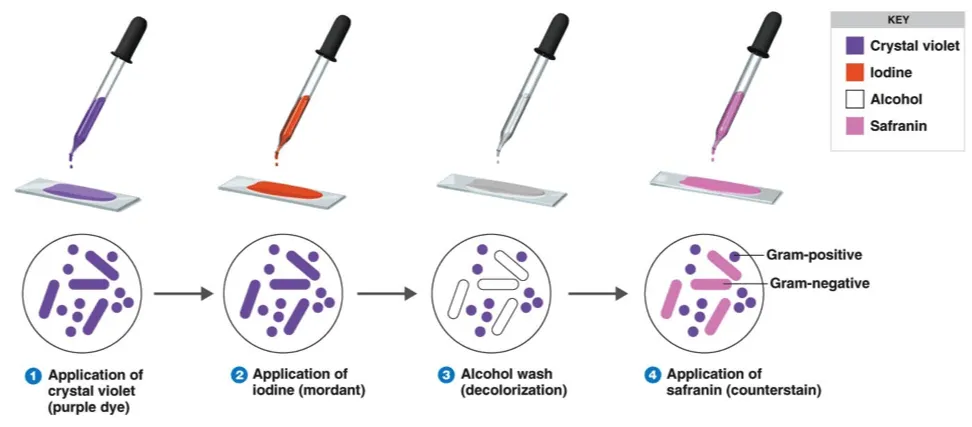
1- Apply the basic dye (ex: crystal violet) to the smear to stain it.
2- Add iodine solution (as it increases the interaction between dye and cells so it stains sharply).
3- Wash the smear with ethanol or acetone to be decolorized.
4- The previous step makes the differential aspect of Gram stains. Gram positive bacteria retain crystal violet and become colourless.
Finally the smear is counter-stained with a basic dye that must be different in color from Crystal violet like safranin which changes the colour of Gram negative bacteria from pink to red and leaves the colour of Gram positive bacteria dark purple.
PraxiLabs provides a 3D virtual simulation Gram Staining laboratory, allowing you to conduct any experiment easily and clearly with PDFs to explain the theoretical scientific material of the experiment, simplistic videos to explain the steps and more features. Create your free account and try it now!
4. Isolation Techniques in Microbiology
In nature, microorganisms are found and mixed with the different forms and kinds of life, but in many cases we need to identify a certain microorganism, for example there are many pathogenic microorganisms that can cause severe diseases, so we need to identify and control the infectious microbe in laboratories by isolate it then let it grow in pure culture that contains only 1 specie of microorganism.
We can isolate different types of pathogens from body tissues or fluids such as blood, urine, pus, sputum, faces, spinal fluid, stomach fluids, bile and pleural fluids.
The following isolation methods are the most common and employed to isolate microbes from mixed cultures:
- Streaking
- Plating
- Dilution
- Enriched procedure, and
- Single cell technique.
We will clarify in detail the first 2 methods (streaking techniques in microbiology) and (plating techniques in microbiology).
-
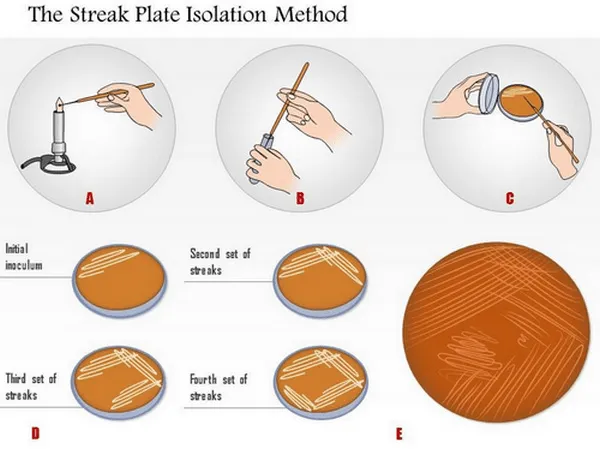
Streaking Techniques in Microbiology
Streaking is one of the most commonly used isolation microbiology techniques. It is used to separate and isolate a pure strain from a species of microorganism (bacteria). We can take the needed samples from the resulting colonies and also we can grow the microbiological culture on a new plate so that the wanted microorganism can be isolated, identified and tested.
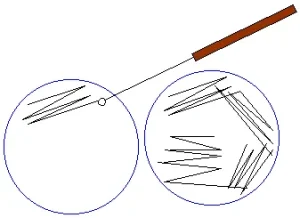
The method steps depends on:
- Pour a suitable sterile medium into a sterile petri dish then allow the medium to solidify.
- Streak a small amount of the growth (coming from bacterial suspension or broth culture) by using sterile means needle or loop or bent glass-rod.
- Make sure that you streak back and forth across the agar surface until about one third of the diameter of the plate has been covered.
- Then, the sterile needle is flamed and streaking is done at right angles to and across the first streaking. This drag the microorganism out in a long line from the first streak.
- Flame the needle again flamed and streak again for the third time at the right angles to the second streak and parallel to the first.
There are many Types of streaking techniques in microbiology like quadrant streaking \ T-streaking \ continuous streaking \ radiant streaking.
-
Plating Techniques in Microbiology
Plating techniques in microbiology are used mainly to separate microorganisms which are found in a small sample volume and spread over the surface of a plate of an agar plate and the result is the formation and the distribution of discrete colonies across the surface of the agar.
The steps of plating method include:
- Dilute a mixture of microorganisms until only a few hundred bacteria are left in each millilitre of the suspension.
- Place a small amount of the dilution in a sterile Petri dish by using a sterile pipette or loop.
- Let the melted agar medium cool to about 45°C and then pour it into the plate.
- Mix well the microorganism and agar and when the agar is solidified the individual bacterium will be held in place and will grow to visible colonies.
Try to conduct Bacterial Plating out Technique Experiment (Streak plate method) in our virtual lab for Free
Medical Microbiology Techniques

There are many medical microbiology techniques that are used widely in the laboratories to study the pathogenic microorganisms (their characteristics – mechanism of infection – growth – transmission and more).
Beside the physical examination and the medical history of the patient, the medical microbiology techniques are mainly used for the Diagnosis of infectious disease.
The most common medical identification techniques include:
- Microbial Culturing Techniques
- Biochemical Tests
- Microscopy
- Polymerase Chain Reaction
Microbial Culturing Techniques
As we explained previously
Biochemical tests
Fast and simple biochemical tests are used to identify infectious pathogens. For example, in the case of bacterial identification, the tests depend on the presence of acids, gasses and alcohols to detect the growth of bacteria.
Examples of Biochemical tests used for bacterial identification:
- Catalase Test
- Antibiotic Sensitivity Test
- Coagulase Test
- Indole Test
- Oxidase Test
- CAMP Test
- Starch hydrolysis test
- Bile Esculin Agar Test
- Taxos P (optochin sensitivity testing)
- Taxos A (bacitracin sensitivity testing)
- Nitrate Broth
- Methyl Red / Voges-Proskauer (MR/VP)
- Urease test
- Sulfur Indole Motility Media (SIM)
The catalase test is used to facilitate the determination of catalase enzyme in bacteria.
It is specifically used to:
- Differentiate between catalase-negative Streptococcaceae and catalase-positive Micrococcaceae.
- Differentiate between genera species.
- Differentiate among certain Enterobacteriaceae.
- Differentiate between gram-positives organism like Aerococcus urinae and gram-negative organisms such as Campylobacter.
- neutralize the bactericidal effects of H2O2 hydrogen peroxide by increasing the rate of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) breakdown into oxygen and water (2H2O2 + Catalase → 2H2O + O2).
PraxiLabs provides a group of Biochemical tests like indole test \ coagulase test \ catalase test \ oxidase test.
Microscopy
The examination by using microscopes (like compound light, fluorescence and electron microscopes) is important and useful in the identification of the different pathogens and considered as one of the important microbiology techniques. This method provides accurate observation of microbes and cellular features.
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) procedure is the most used molecular technique to determine and study microbes. If we compare PCR technique to other techniques like sequencing , we will find that PCR is fast, accurate, definitive and reliable.
For more information about PCR, read our blog What Are The Three Basic Steps of Conventional PCR?
New Techniques in Microbiology (MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry)
Rapid identification of microorganisms in the clinical microbiology laboratory by using MALDI-TOF MS is considered one of the important new microbiology techniques and can be of important and great value for the process of optimal patient management strategies selection for infections caused by viruses, bacteria, mycobacteria, fungi, and parasites.
In the first experiment of MALDI-TOF MS, it succeeded in identifying bacteria directly from the whole colonies dependent on protein biomarkers. After that a big number of developments and advancements have been made on whole-organism MALDI-TOF MS. The protein biomarkers which are measured in microorganisms mass spectrometry are considered as highly expressed proteins and they are responsible for functions like ribosomal translation and transcription.
These diagnostic methods in microbiology that are used for the rapid identification of microorganisms in clinical samples enables expedient de-escalation from broad-spectrum agents to targeted antimicrobial therapy. The torn to this specific therapy decreases risks of antibiotics, normal flora disruption, selective pressure and toxic side effects. There is a necessary need for new technologies and advancements in microbiology, specially in clinical microbiology and particularly for infections of the bloodstream that are related to the highest of all infections.
Advancements in Microbiology
Now we will review some of the latest discoveries and recent developments in microbiology:
Dormant strains of bacteria that have previously adapted to cope with certain temperatures are switched back on during climatic change
“Understanding the relative importance of acclimation, adaptation and species sorting in the assembly and turnover of microbial communities is key to determining how quickly they can respond to temperature changes. Until now, a mechanistic basis of these community-level responses had not been discerned ,” concludes senior author Thomas Bell, Professor of Microbial Ecology at the Georgina Mace Centre for the Living Planet, Imperial College London. “We have found that the resuscitation of functional diversity within a microbial community can allow the whole community to survive in response to temperature changes. Further studies on other microbial communities — such as those residing in water — will support more accurate predictions of the effects of climate change on different ecosystems.”
Discovery of antibody structure could lead to treatment for Crimean Congo Hemorrhagic Fever virus
A research team has discovered important details about how therapeutically relevant human monoclonal antibodies can protect against Crimean Congo Hemorrhagic Fever virus. Their work could lead to the development of targeted therapeutics for infected patients.
PraxiLabs provides more than 50 biology virtual lab that you can access anytime and anywhere. Subscribe and get started now!
 PraxiLabs A virtual world of science
PraxiLabs A virtual world of science






