Last Updated on June 23, 2025 by Muhamed Elmesery
Imagine stepping into a biology lab where you can observe enzyme reactions, manipulate variables like temperature and pH, and watch biological processes unfold — all without breaking a test tube or handling a single chemical.
Welcome to the world of enzyme simulation lab, where cutting-edge technology brings biochemistry to life through interactive, immersive, and virtual experiments.
In this blog post, we will learn more about what is enzyme simulation lab, enzyme simulation lab objectives, how do you investigate enzyme activity, enzyme simulation lab and STEM education, explore some enzyme reactions in Praxilabs, and more!
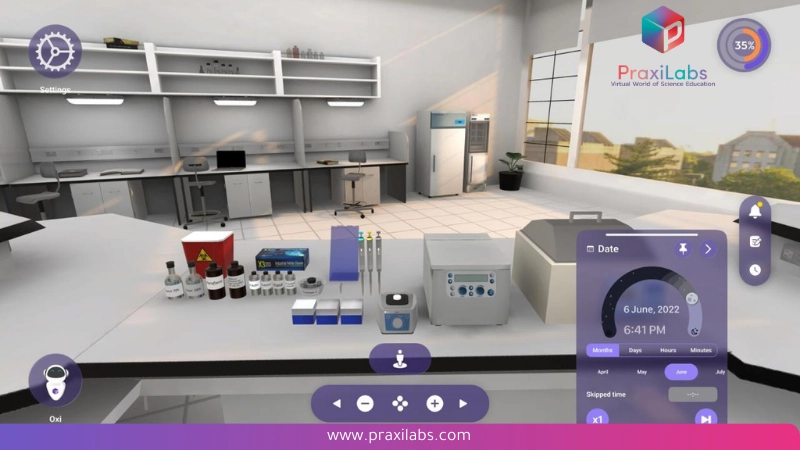
Table of Contents
What is enzyme simulation lab?
An enzyme simulation lab is a virtual lab environment that allows students to visualize and conduct enzyme reactions without needing a physical lab setup. Students will explore how enzymes work, investigate the factors that affect their activity, and more in an interactive, and safe environment.
All you need to try an virtual enzyme lab to create an account on one of the trusted virtual labs platforms that provide enzyme lab simulation.
Enzyme simulation lab objectives
By the end of the enzyme activity simulation lab, students will be able to:
1. Understand the factors that enzyme activity such as:
- Temperature.
- PH level.
- Substrate concentration.
- Enzyme concentration.
- Inhibitors.
2. Understand various biochemical processes involved in the production of the enzyme.
3. Describe how enzyme production can be measured.
4. Differentiate between bacterial species such as Neisseria, Moraxella, Campylobacter and Pasteurella from other bacteria.
5. Handle the required instruments and consumables used in the present experiments.
6. Determine the optimum conditions for detecting enzyme activity.
7. Understand the mechanism of enzyme action.
8. Describe the actual role of different enzymes in chemical reactions as catalysts.
How do you investigate enzyme activity?
To investigate enzyme activity, you need to do an experiment that qualitatively detects the enzyme. In addition, the effect of temperature and pH value on the enzyme activity.
This can be done in a virtual science lab through a simulation. Here’s how the process works:
1. Choose an Enzyme and Substrate
- Example: Detection of salivary amylase activity.
- Enzyme: Salivary amylase.
- Substrate: Starch.
2. Set a Clear Aim
Aim: to examine the effect of the amylase enzyme on starch breakdown and investigate factors that affect the activity of the amylase enzyme (such as temperature, pH, and source of amylase).
3. Run the Experiment
In the virtual lab, you will do the following steps:
1. Starch digestion by salivary amylase using iodine solution.
2. Starch digestion by salivary amylase using Benedict’s reagent.
3. Effect of temperature on starch digestion by salivary amylase.
4. Effect of pH on starch digestion by salivary amylase.
4. Collect and Analyze Data in Enzyme virtual lab worksheet
- Record reaction rates under each condition.
- Plot graphs (e.g., rate vs. temperature, rate vs. pH).
- Look for the optimum point where the enzyme is most active.
5. Draw Conclusions
- Identify the optimal conditions for enzyme activity.
- Explain why activity drops at high or low extremes (e.g., due to denaturation or structural change).
For more understanding, You can try PraxiLabs virtual lab (Amylase test) .. Create your free account now and try it!
Enzyme simulation lab and STEM education
Integrating enzyme virtual lab simulation into STEM education is a great opportunity for enhancing your students’ understanding rate of biological concepts.
This integration brings several features, such as:
- Safety.
- Cost-effective.
- Repeatability.
- Accessible anywhere and anytime.
- Encouragement of inquiry-based learning.
- Development of 21st century digital science skills.
- An interactive and immersive 3D environment.
- Alignment with various learning styles.
- Hands-on experience.
- Real-time feedback.
PraxiLabs provides instant and unlimited access to several STEM simulations you may need from anywhere, without the hassle of going to the laboratory. Let your young scientists enjoy their journey, anytime!

Explore some enzyme reactions in Praxilabs
PraxiLabs provides several immersive and interactive biology simulations enzymes labs to enhance student’s learning rate of biochemistry concepts. Let’s explore some enzyme reactions in PraxiLabs:
Urease Test
In the urease enzyme simulation lab, your students are going to learn how to detect the presence of urease enzyme.
Urease test is mainly used to determine the ability of microorganisms to degrade urea to carbon dioxide and ammonia by means of the enzyme urease, and to distinguish urease-positive Proteae from other Enterobacteriaceae.
By the end of the experiment students will be able to:
- Become proficient at performing the urease test consistently and accurately.
- Differentiate between different members of lactose non-fermenting enteric microorganisms.
Amylase Test
By the end of the Amylase Test, you will be able to:
- Handle the required instruments and consumables in the present experiments.
- Explain how iodine and Benedict’s reagent indicate starch hydrolysis.
- Evaluate the effects of temperature and pH on the rate of enzymatic digestion of starch by amylase.
Catalase Test
Give your students the chance to:
- Understand the biochemical process of hydrogen peroxide detoxification by aerobic bacteria through the production of the enzyme catalase.
- Describe how catalase production can be determined.
- Perform the Catalase Test accurately.
Coagulase Test
Teach your students how to:
- Understand the biochemistry of the enzyme coagulase.
- Explain how coagulase confers a survival advantage to bacteria that produce this enzyme.
- Describe how pathogenic species of Staphylococci can be differentiated from nonpathogenic species.
- Conduct a coagulase test.
Oxidase Test
By the end of the oxidase test, your students will be able to:
- Become proficient at performing the oxidase test consistently and accurately.
- Determine if an organism possesses the cytochrome oxidase enzyme.
- Differentiate Neisseria, Moraxella, Campylobacter and Pasteurella species (oxidase positive) from other bacteria.
- Differentiate pseudomonads from related species.
Visit Our Ever-Expanding Catalog of 3D science simulations and Enhance Your Students’ Learning Outcomes!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of the enzyme lab?
The purpose of the enzyme lab is to teach students concepts such as the mechanism of enzyme action, factors that affect the enzyme activity (e.g., temperature, PH – concentration), biochemical process involving enzyme production, and more.
How do you measure enzyme activity in a lab?
Enzyme activity can be measured in a lab by observing either:
- The rate at which a substrate disappears.
- The rate at which a product forms.
 PraxiLabs A virtual world of science
PraxiLabs A virtual world of science






