Last Updated on August 22, 2025 by Muhamed Elmesery
Bernoulli equation, or the incompressible steady flow energy equation, is considered one of the most well-known equations in physics ( fluid mechanics) and it explains the conservation of mechanical work-energy. The equation was published in 1738 by Daniel Bernoulli (a Swiss physicist) to help us understand fluid flow.
Daniel Bernoulli was born on February 8th, 1700, in the Netherlands. He studied mathematics and medicine under the guidance of his father Johann Bernoulli.
In this article, we will discuss Bernoulli equation, principle, derivation, application and more.
Get started Praxilabs for FREE
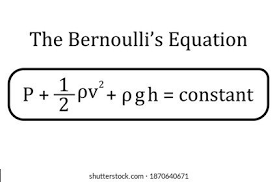
Table of Contents
Bernoulli Equation
- P is the static pressure (the pressure of the fluid).
- ρ is the density.
- V is the velocity.
- G is the gravitational acceleration.
- H is the elevation of the fluid.
Bernoulli’s theorem describes the relation between velocity, pressure, and elevation of a flowing fluid in a streamline.
It states that the dynamic pressure plus the static pressure in the flow, one half of the density (r) times the velocity (V) squared, is equal to a constant throughout the flow. The constant is called the total pressure of the flow (pt).
Or simply, the Bernoulli equation states that the sum of the potential, kinetic, and flow energies of a fluid is constant in a streamline in steady flow.
Note:
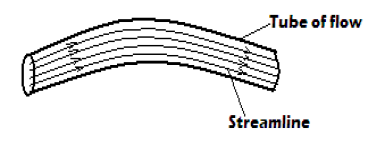
The streamline in steady flow is the path traced by a single particle within the fluid.
The following figure shows the streamline in steady flow:
To apply Bernoulli’s equation:
- The flow must be steady (Velocity, density, and pressure must not change at any point in the streamline).
- The flow must be incompressible: even when the pressure varies, the density must remain constant along the streamline.
- Friction by viscous forces must be negligible or minimal.
Note:
Incompressible flows are gasses and gasses with a low Mach number and constant fluid density, regardless of the pressure flow. By using incompressible flow, we will have the simplest form of Bernoulli’s equation.
Bernoulli Differential Equations
A Bernoulli differential equation is a specific type of ordinary differential equation that can be expressed in the form:
y′+P(x)y=Q(x)yn
Where:
n is a real number (except for 0 or 1), because it is notable for its non-linear nature and if n=0 or n=1 then the equation is linear.
Bernoulli equation for V
In Bernoulli’s equation, we can find the velocity of the fluid
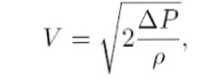
Where:
- ρ is the density of the fluid.
- P is the measured pressure.
What is Bernoulli’s Principle ?
Bernoulli’s principle states that an increase in the velocity (the speed of a fluid) occurs simultaneously and must be accompanied by a decrease in the potential energy of the fluid (or the static pressure).
Bernoulli’s principle can be derived from the conservation of energy principle. In case of steady flow, the sum of energy forms in a fluid will remain the same at all points of that streamline. While all the energy remains constant, an increase in the fluid velocity will imply that there is an increase in the kinetic energy or dynamic pressure. This happens with a decrease in the potential energy (the static pressure and internal energy).
Bernoulli’s Principle Formula
Bernoulli’s equation formula is considered a relation between pressure, potential energy, and kinetic energy of a fluid.
The formula given is as follows:
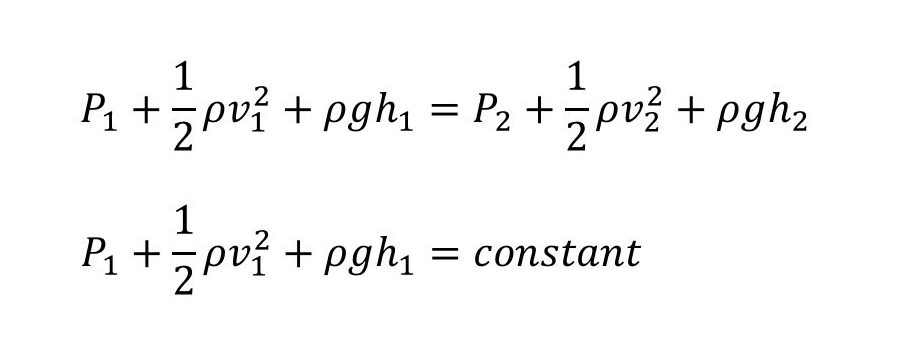
The Bernoulli equation can be considered to be the conservation of energy principle for the flowing fluids. Bernoulli effect is the lowering of fluid pressure in cases where the velocity is increased. In the case of high velocity flow through the constriction, the kinetic energy must increase at the expense of pressure energy.
Limitations on the Use of Bernoulli Theorem
The Bernoulli equation is applicable to steady flow as we explained before, but in some cases we can’t use the Bernoulli equation.
The Bernoulli theorem is not applicable in a flow section like machines (e.g., fan or turbine or pump), because these machines can damage the streamlines and make energy interactions with the fluid. So in these cases, the energy equation should be used instead of Bernoulli equation.
The equation also should not be used for significant temperature change flow sections like cooling or heating sections, because the gas density is inversely proportional to the temperature.
Every flow involves some friction and if the frictional effects are not be negligible, the Bernoulli theorem is not applicable in this case.
So, the Bernoulli equation should not be used in the flow of:
- Sudden expansion.
- Heating section.
- Valve.
- Fan.
- Narrow long tube.
Bernoulli Equation Derivation
We can drive Bernoulli differential equation as follows:
We will consider that we have a pipe with a varying height and diameter through which an incompressible fluid is flowing. The relationship between the areas of cross-sections A, pressure p the speed of the flow v, and the height h at two different points 1 and 2 is described in the following figure:
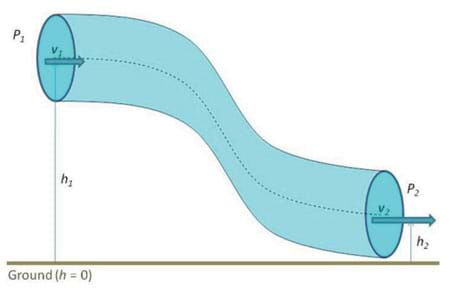
Assumptions:
- The incompressible fluid density remains constant at both points.
- The fluid energy is conserved because there are no viscous forces in the fluid.
So, the work done on the fluid is given as:
- dW = F1dx1 – F2dx2
- dW = p1A1dx1 – p2A2dx2
- dW = p1dv – p2dv = (p1 – p2)dv
We know that the work done on the fluid was due to the conservation of change in both the kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy
The change in kinetic energy of the fluid is given as:
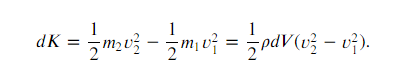
The change in potential energy is given as:
- dU = m2gy2 – m1gy1 = ρdvg(y2 – y1)
Then, the energy equation is given as:
dW = dK + dU
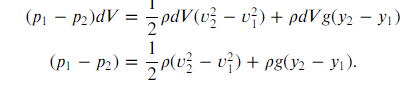
And finally by rearranging the above equation, we get
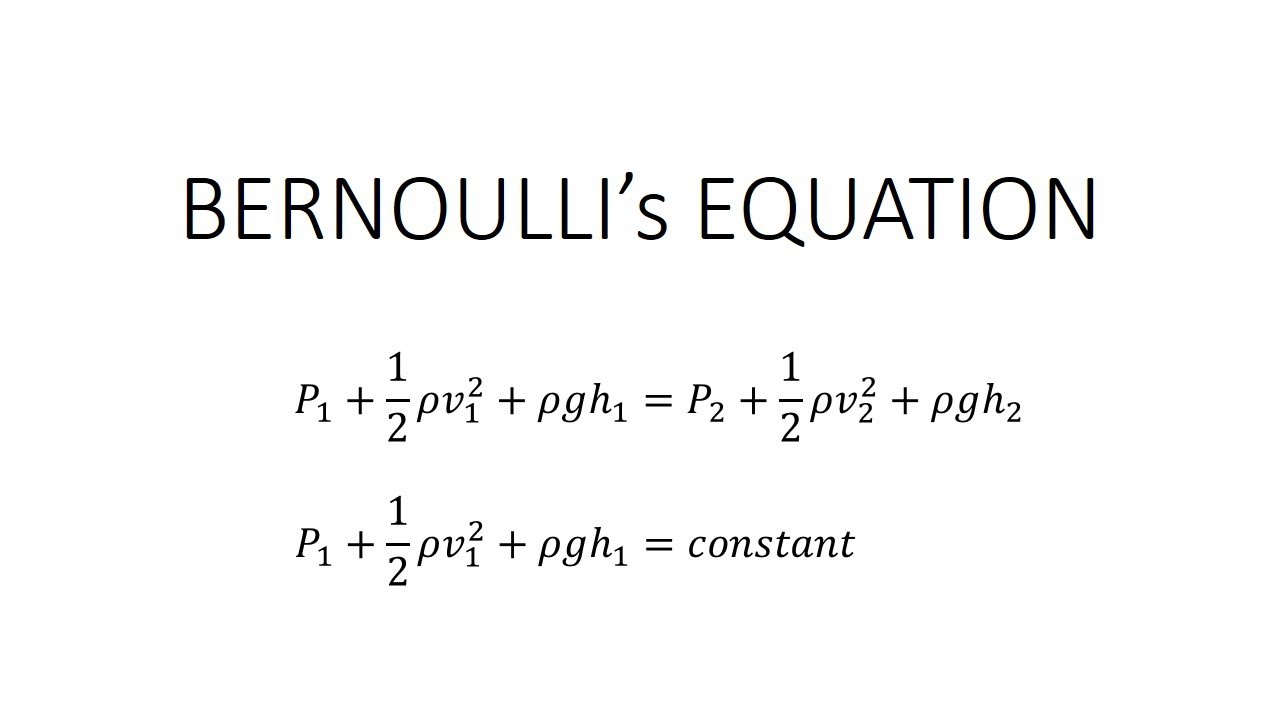
For more understanding, watch the following video about Bernoulli equation derivation
PraxiLabs virtual science labs enable you to conduct various laboratory experiments in physics, chemistry, and biology online anytime and anywhere. Create your free account and try our virtual labs now.
Bernoulli Equation Applications
Bernoulli’s equation has many applications. For example, we can use it to explain how planes generate lift, to calculate the velocity of fluid flow, or why ships have to run away from each other as they pass, and other applications that we find in our daily lives. We will go over in detail some of the most popular applications of bernoulli’s theorem.
-
Bernoulli Theorem application in fluid mechanics
The Bernoulli equation is applied to all incompressible fluid flow problems. The Bernoulli equation can be applied to devices such as the orifice meter, Venturi meter, and Pitot tube and its applications for measuring flow in open channels and inside tubes.
Venturi meter is a device that is based on Bernoulli’s principle and used to determine the rate of flow through a pipe. It works by measuring the pressure drop across a section near the pipe. For an incompressible fluid, reducing the diameter will increase the fluid flow velocity.
Note: Bernoulli’s principle states that there must be a pressure drop in the region of the reduced diameter. This phenomenon is known as the venturi effect.
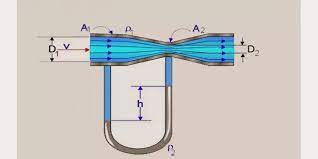
Venturi meter
-
Application of Bernoulli’s equation in pumps
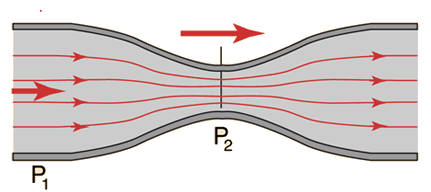
As we mentioned before,the speed of a fluid flow can be measured by devices like Venturi meter, which is used to reduce the diameter of the flow and placed into a pipeline.
The maximum possible discharge rate for a tank with an opening or a spout at the base can be calculated directly by Bernoulli’s equation, and it has been found to be proportional to the square root of the height of the liquid in the tank (this is Torricelli’s law) and this shows that Torricelli’s law is compatible with Bernoulli’s principle. Viscosity reduces the rate of discharge.
-
Application of Bernoulli’s Theorem in Aeroplanes
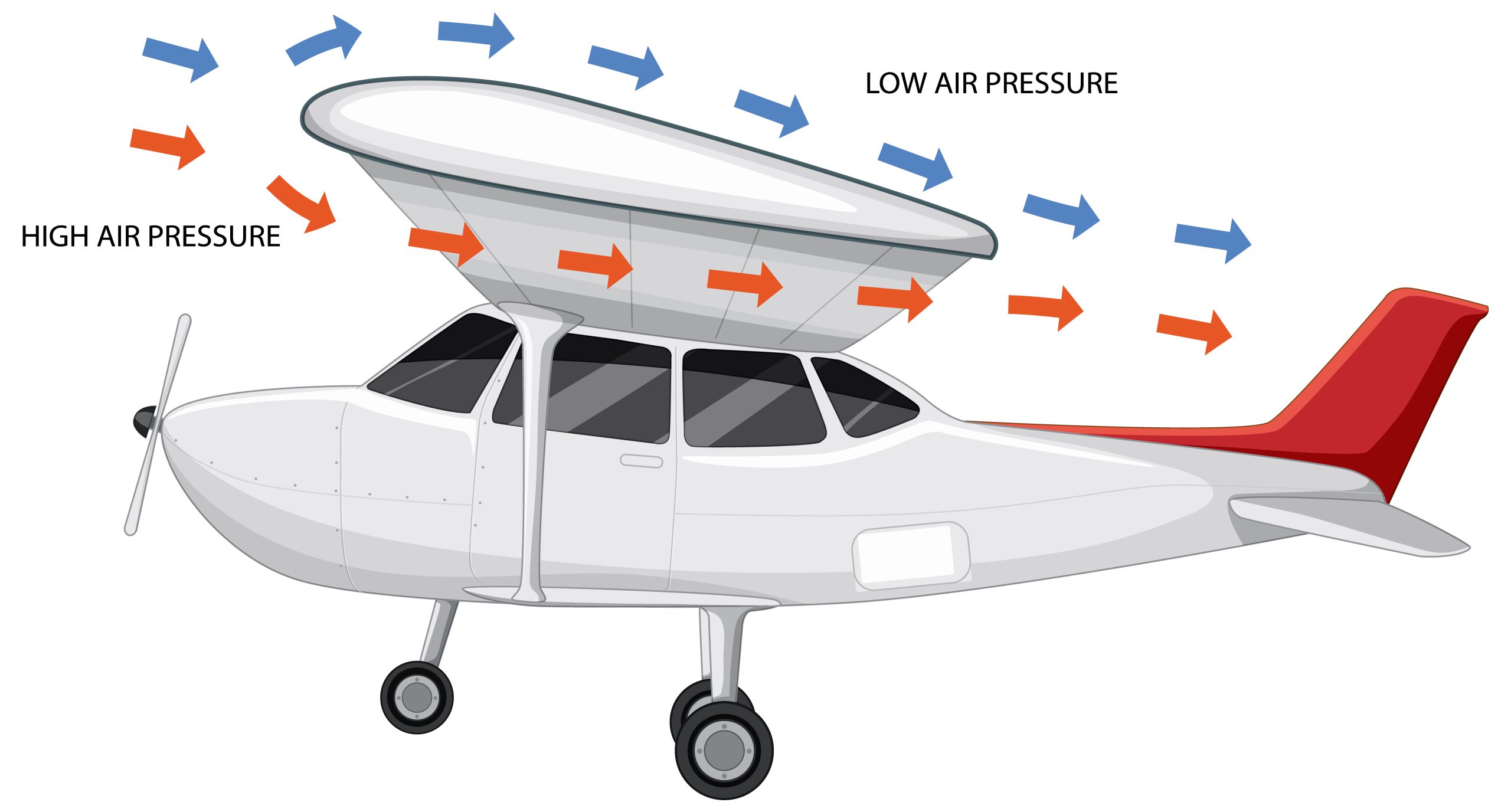
How aircraft wings generate lift can be explained by Bernoulli’s equation for fluids. In the case of flight, the fluid flowing above the wing of the aircraft moves faster than the flowing under the wing, and according to Bernoulli’s principle this causes the creation of a region of low pressure above the surface of the air and a region of high pressure under the plane and this pressure difference is what generates altitude.
That is, we can explain the reason for the shape of the wings and their upward curvature (according to Bernoulli’s theory) that the air passes at a higher speed on the upper surface than the lower one. The difference in air velocity is calculated using Bernoulli’s principle of difference in pressure.
-
Pressure detection
In some cases of fluid flows, we know the velocities at two points of the streamline and pressure at only one point. The unknown is the pressure at the other point of the fluid.
So in this case (if the Bernoulli equation applies to it ) we can use Bernoulli’s Equation to find the unknown pressure.
-
Velocity detection
In cases where the elevation and pressure at two points of the streamline are known and velocity at one point is also known, and we want to find the unknown velocity, Bernoulli’s Equation is applied to calculate and find the required velocity.
For example: the flow through a siphon
In this case, we need to find the velocity with which the fluid leaves the siphon. By applying Bernoulli’s Equation between the reservoir surface and the siphon exit point where the fluid leaves the tube, pressure at both points is the same and equal to the atmospheric pressure, and the velocity at the reservoir is negligible because the reservoir is large. We can calculate the velocity at the exit point by using the values of elevation at the two points.
-
Application of Bernoulli’s equation in medicine
In echocardiography, Bernoulli’s principle can be applied when interpreting blood flow to describe a localized pressure decrease produced by high flow rate near blockages.
For clinical medicine, the equation is used for an easy estimation of pressure gradients from velocity.
Bernoulli’s equation can also be used in the venturi mask.
The venturi mask is a medical oxygen device that delivers oxygen concentration to patients on controlled oxygen therapy. The mask has a tube that is connected to a nozzle which connects to a supply of pure oxygen. The tube that is directly connected to the mask has a small window which allows room air to flow into the mask.
The venturi mask can control the amount of oxygen that flows in, along with pure oxygen delivered from its connected nozzle.
Venturi masks use the Bernoulli principle, As oxygen flows into the tube, it creates a decrease in pressure due to oxygen passing through a narrow opening of the tube. The air is allowed to flow into the mask by the drop of pressure, mixing with the pure oxygen from the nozzle, which is the consequence of Bernoulli’s principle.
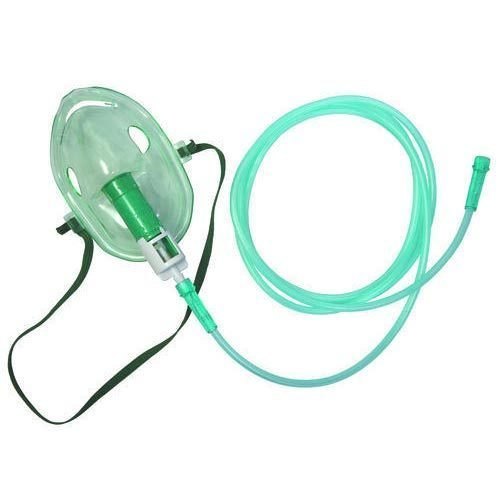
Other Applications of Bernoulli’s Principle
- Bernoulli’s theory is used to study the unstable potential flow used in the theory of ocean surface waves and acoustics.
- When we stand at a railway station and a train comes in, we tend to fall towards the train. We can explain this using Bernoulli’s principle. As the train passes, the speed of the air between us and the train increases. Hence, from the equation, we can say that the pressure is decreasing. So the pressure from the back pushes us towards the train and that depends on the Bernoulli effect.
- The Bernoulli equation also explains how a Bunsen burner works. When the gas valve is opened, the gas flows into the barrel at a high velocity. According to Bernoulli’s theory, this high velocity creates a low pressure area in the barrel (which draws air through the regulator) allowing the gas to burn more efficiently.
- Many flow meters are based on Bernoulli’s principle to determine the velocity of a flowing fluid. The most famous of these devices is the Pitot-Static Tube, which is used in aircraft to measure flight speed.
- Bernoulli’s principle also applies to swinging a cricket ball. During the match, players constantly polish one side of the ball. After some time, one side is completely rough and the other is still smooth. Hence, when the ball is thrown in the air, the velocity on one side of the ball is faster than the other, due to this difference in smoothness. And this leads to a difference in pressure between the two sides. This causes the ball to spin (“swing”) as it travels through the air.
Bernoulli Equation Assumptions
For Bernoulli’s equation to be applied, the following assumptions must be met:
- The flow must be steady. (Velocity, pressure and density cannot change at any point).
- The flow must be incompressible – even when the pressure varies, the density must remain constant along the streamline.
- Friction by viscous forces must be minimal.
Example of Bernoulli Differential Equations
Try to solve the Bernoulli differential equation: y′ + y = xy2
Solution:
Rewrite the equation in standard form:
y′+y = xy2
Divide through by y2:
\frac{y’}{y^2} + \frac{y}{y^2} = x
Simplified:
y^{-2}y’ + y^{-1} = x
Substitute v = y{-1}:
Derivative:
\frac{dv}{dx} = -y^{-2} \frac{dy}{dx}
Rewrite the original equation:
-\frac{dv}{dx} + v = x
Rearrange:
\frac{dv}{dx} – v = -x
- Find the integrating factor:
\mu(x) = e^{\int -1 \, dx} = e^{-x}
- Multiply through by the integrating factor:
e^{-x} \frac{dv}{dx} – e^{-x} v = -xe^{-x}
- Simplify:
\frac{d}{dx} \left( e^{-x} v \right) = -xe^{-x}
- Integrate both sides:
e^{-x} v = \int -xe^{-x} \, dx + C
- Using integration by parts:
\int -xe^{-x} \, dx = -xe^{-x} – \int e^{-x} \, dx = -xe^{-x} + e^{-x}
- Thus:
e^{-x} v = -xe^{-x} + e^{-x} + C
- Simplify:
v = -x + 1 + Ce^{x}
- Back-substitute v = y{-1}:
y^{-1} = -x + 1 + Ce^{x}
- Solve for y:
y = \frac{1}{-x + 1 + Ce^{x}}
Source: How to Solve Bernoulli Differential Equation
Gamified learning experiences with Bernoulli’s equation
Gamification is the method that depends on using game-design elements and game mechanics in non-game contexts. Some researchers suggest that it could also be used in web-based education as a tool to increase student motivation and engagement.
For example, using gamified learning elements in teaching Bernoulli’s equation can motivate and encourage learners to participate in the learning process and thus improve their learning outcomes and also enhance their engagement and motivation.
In an attempt to verify those theories, researchers conducted a study “Gamifying Learning Experiences: Practical Implications and Outcomes” they designed and developed a gamification plugin for a well-known e-learning platform. They conducted an experiment using this plugin in a university course, collecting quantitative and qualitative data in the process.
Their findings suggest that some common beliefs about the benefits obtained when using games in education can be challenged. Students who completed the gamified experience scored better in practical assignments and achieved higher overall scores, but their findings also suggest that these students performed poorly on written assignments and participated less in class activities, although their initial motivation was higher.
Interactive simulations of Bernoulli’s equation
Virtual lab simulations can enrich the experimentation process, help students to understand Bernoulli’s equation.
Educational virtual labs for fluid mechanics such as the interactive simulations of Bernoulli’s equation simulate the water flowing through a pipe. You can adjust the outlet height, outlet pipe diameter, inlet pressure, and inlet velocity using the sliders.
Virtual labs for Online experiments with fluid flow phenomena provide a wide range of interactive features:
- Interactive 3D virtual labs provide students with tools that allow for more focus, attention, and engagement. Students stay interested, alert, and absorb information more easily.
- Virtual labs eliminate potential safety hazards associated with handling hazardous materials or conducting experiments that require specialized equipment. Students can learn and experiment in a safe environment, reducing the chances of accidents or mishaps.
- By using virtual labs, you can save time and effort, as they eliminate the need to move between different laboratories. Students can access experiments and learning resources without the need for setup or cleanup, allowing them to focus more on the core learning objectives.
- Virtual labs provide a virtual learning and teaching environment that aims to develop practical skills and learning outcomes.
- Students can conduct experiments with 24/7 unlimited accessibility and repeat virtual experiments as many times as needed until they grasp and understand all the information.
- Since virtual simulations are accessible via the Internet, students can perform numerous experiments without being confined to specific locations or times, unlike when using real laboratories.
PraxiLabs simulation lab enable you to conduct various laboratory experiments in physics, chemistry, and biology online anytime and anywhere. Create your free account and try PraxiLabs virtual labs now.
 PraxiLabs A virtual world of science
PraxiLabs A virtual world of science






