Last Updated on August 22, 2025 by Muhamed Elmesery
Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (PAGE) is a fundamental technique in the realm of molecular biology, enabling the separation and analysis of macromolecules such as DNA, RNA, and proteins based on their size and charge. As a cornerstone of scientific research and clinical diagnostics, understanding the intricacies of this method is essential.
In this blog, we’ll delve into the world of Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis, exploring common questions and providing insightful answers to demystify this powerful tool.
Table of Contents
What is the Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis PAGE?
Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (PAGE) is an electrophoretic technique that is used mainly for protein analysis by separating proteins, nucleic acid fragments (smaller than 100bp), and polypeptide chains depending on their electrophoretic mobility. It is widely used in molecular biology, biochemistry, genetics, forensic chemistry, and biotechnology.
What is the SDS-PAGE of a protein?
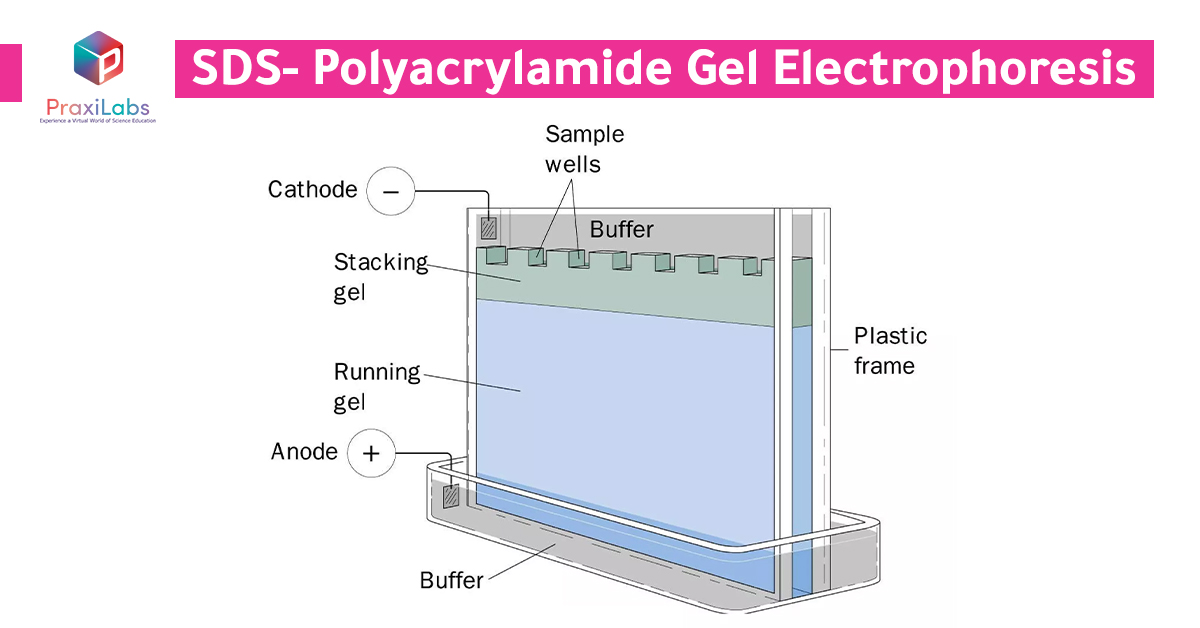
SDS-PAGE (SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis) is an electrophoretic technique that separates polypeptide chains according to their molecular weights (Mr). This method uses polyacrylamide gel containing sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) which is added to the system in order to provide denaturing conditions.
You can tell from its name that the technique utilizes polyacrylamide gel containing sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS). SDS in the sample and the gel cancels the effect of intrinsic electrical charge of the sample proteins. All proteins acquire a negatively charged rod like structure, so separation becomes largely dependent on Molecular weight of sample proteins.
The gel used in SDS PAGE can be divided into stacking gel and separating gel. Stacking gel (acrylamide 5%) is poured on top of the separating gel (after solidification) and a gel comb is inserted in the stacking gel. The acrylamide percentage is chosen in accordance with the size of target proteins in the sample.
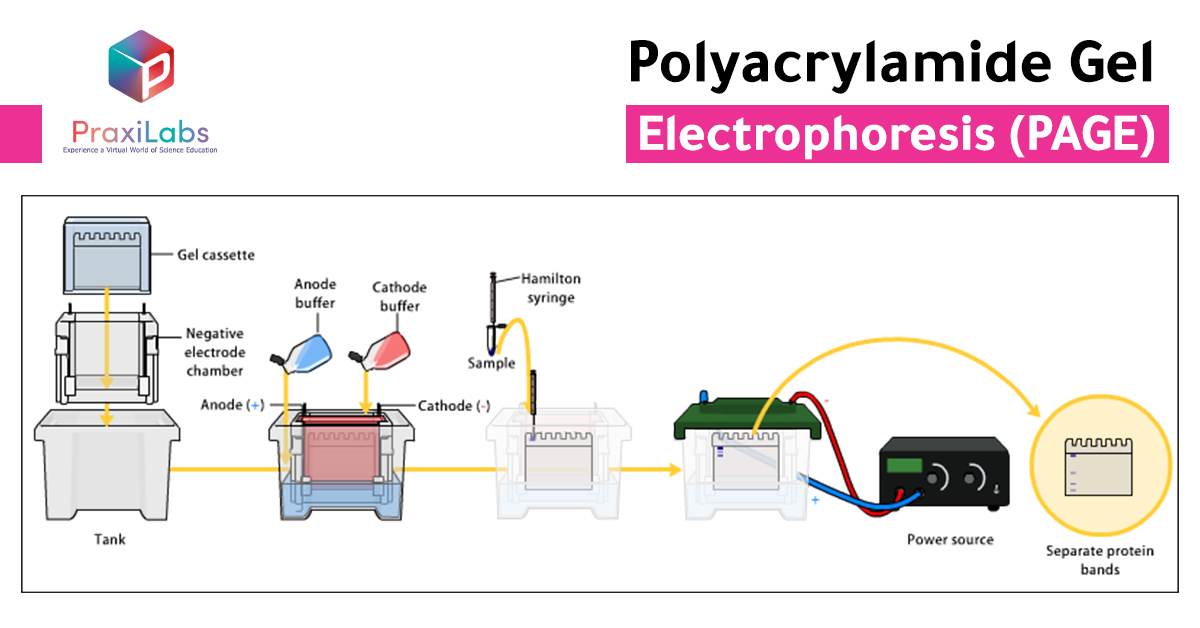
How does polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) work?
The main principle of Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis PAGE is to separate molecules (proteins, or polypeptides, or nucleic acids) by passing them through the pores of a polyacrylamide gel using an electric current. To achieve this, an acrylamide–bisacrylamide mix is polymerized (polyacrylamide) by the addition of ammonium persulfate (APS).
The reaction, which is catalyzed by tetramethylethylenediamine (TEMED), forms a net-like structure with pores through which analytes can move. The higher the percentage of total acrylamide included in the gel, the smaller the pore size, hence the smaller the proteins that will be able to pass through. The ratio of acrylamide to bisacrylamide will also impact pore size but this is often kept constant. Smaller pore sizes also reduce the speed at which small proteins are able to move through the gel, improving their resolution and preventing them from running off into the buffer rapidly when current is applied.
Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, how it works, technique variants and its applications, Analysis & Separations from Technology Networks. Available at: (Accessed:01 July 2024).
What does the SDS-PAGE tell you?
The SDS-PAGE provides us with information on the mass, charge, purity, or presence of a protein by separating polypeptide chains according to their molecular weights.
In PraxiLabs, we provide several virtual labs simulations for protein electrophoresis such as:
- Protein Electrophoresis (Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis – PAGE)
Learn polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis protocol and practice proper sample preparation for SDS-PAGE (SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis.
- 2D Protein Electrophoresis (Isoelectric Point Focusing, PAGE)
Learn how to extract the cellular proteome from a sample, followed by its isoelectric focusing and SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis.
Understand how to detect a specific protein in a sample using electroblotting of proteins into nitrocellulose membrane.
Learn how to separate and identify DNA or RNA molecules by size, using an electric current.
Why do we use PAGE for protein electrophoresis?
We use PAGE for protein electrophoresis to obtain high resolution separation of complex mixtures of proteins by separating polypeptide chains according to their molecular weights.
Applications of Protein Gel Electrophoresis:
Once proteins have been separated by gel electrophoresis, they can be utilized for a number of downstream applications including:
- Determining the size and IP of proteins.
- Enzymatic assays.
- Further purification.
- Transfer to a membrane for immunological detection (immunoblotting or western blot).
- Elution and digestion for mass spectrometric analysis.
- Serum protein electrophoresis is conducted when a patient has an abnormal result on a total protein or albumin blood test or has symptoms of diseases that are associated with abnormal protein production, such as multiple myeloma or multiple sclerosis.
Ready to revolutionize your biology education? Dive into PraxiLabs’ virtual labs and gain unlimited access to cutting-edge experiments

Discover Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis Virtual labs from PraxiLabs
By the end of this simulation students should be able to:
- Prepare polyacrylamide gel properly according to the size of target proteins. Interpret the results of a successful protein electrophoresis run.
- Learn polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis protocol.
- Practice proper sample preparation for SDS-PAGE (SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis).
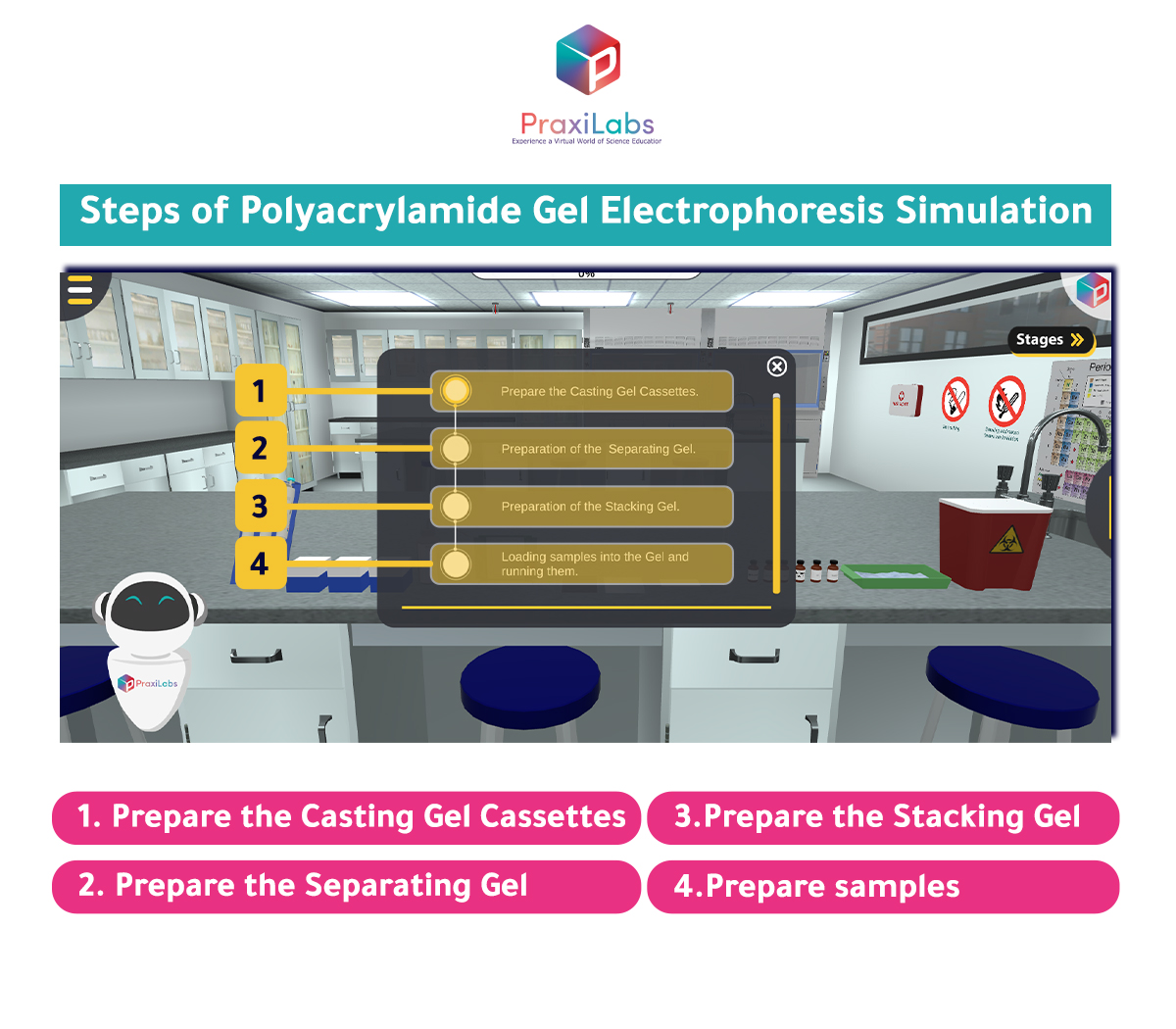
Steps of Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis Simulation
By applying the following steps, you will perform the Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis simulation from PraxiLabs successfully:
First: Gel and buffer preparation
Second: steps of gel casting and sample application
1. Prepare the Casting Gel Cassettes:
- Clean the glass plates with distilled water, dry.
- Clamp two glass plates in the casting frames on the casting stands.
- Pipette distilled water and set aside until the gel is prepared to ensure no leakage.
2.Prepare the Separating Gel:
To prepare a polyacrylamide 12%, 10 ml of separating gel:
- Remove D.W. by turning the cassette upside down on filter paper.
- Pipette The appropriate amount of separating gel solution into the gap between the glass plates. (slowly, thoroughly), leave one 1 cm.
- To make the top of the separating gel be horizontal, fill in distilled water into the gap until it overflows.
- Wait for 20-30 min to let it gelate.
- Discard D.W. by turning the cassette upside down on filter paper.
3.Prepare the Stacking Gel:
To prepare a polyacrylamide 12%,use 5 ml of stacking gel:
- Pipette the stacking gel until overflow.
- Insert the well-forming comb without trapping air under the teeth. Do not move it after insertion.
- Wait for 20-30 min to let it gelate. Make sure a complete gelation of the stacking gel.
- Take out the comb.
- Take the glass plates out of the casting frame and set them in the cell buffer unit.
- Pour the running buffer (electrophoresis buffer) into the inner chamber and keep pouring after overflow until the buffer surface reaches the mark on the outer chamber.
4.Prepare samples:
- Add 5 ul sample in a tube.
- Add 3 ul loading buffer.
- Vortex for 10 seconds.
- Heat them at 95˚C for 3 min.
Using the pipette, Load prepared samples into wells and make sure notto overflow.
- Load 4 ul protein marker into the first lane.
- Cover the top and connect the electrodes.
- Set at 120 volt for one hour and run electrophoresis.
- Stop SDS-PAGE running when the lowermost sign of the protein marker almost reaches the foot line of the glass plate.
General Guidelines for SDS-PAGE (SDS- Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis) Experiment
Increase your Students’ Learning Retention and Engagement!
 PraxiLabs A virtual world of science
PraxiLabs A virtual world of science






