Last Updated on May 15, 2025 by Muhamed Elmesery
Recently, with the emergence of COVID-19 virus, we often hear the term “PCR analysis.” Polymerase Chain Reaction “PCR” is the basic analysis currently used to detect Infected people with COVID-19.
Through the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR analysis), scientists can detect the presence of viruses that cause infection, even when they are present in small quantities in the body. This method contributes to the diagnosis of transmissible viral diseases, as well as to the identification of mutations in various genetic disorders.
PraxiLabs 3D virtual lab of biology provides the PCR experiment within its initiative to support practical colleges, where you can conduct the experiment in the virtual biology lab, which provides science students and professors with a more accurate understanding of PCR meaning.
Try PraxiLabs Virtual Biology Lab for Free
Table of Contents
What is Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)?
Polymerase Chain Reaction is one of the important techniques used to amplify a portion of the DNA chain using very small amounts of materials, where the DNA chain can be multiplied more than a million times.
After the amplification process, a sample of the body fluids or one of its tissues is examined to study DNA, where the DNA contains the genetic code, which is the basis for the process of building body tissues and enzymes responsible for chemical processes, and it is a characteristic of each organism separately. This enables scientists to confirm the presence of strange creatures inside the human body, such as viruses, and determine what type that virus is.
PCR Analysis Experiment Objectives:
The PCR analysis experiment aims to amplify a targeted part of the DNA to a size that may reach up to 10,000 nucleotides, which will allow getting millions of copies of the targeted DNA strand in a short time. Thus, doctors can examine the DNA accurately and make sure that there are extraneous bodies, their type and the amounts of their presence in the patient’s body.
PCR Analysis Experiment Steps:
The experiment of the Polymerase Chain Reaction is divided into three main steps and begins from the preparation of the master mix, where in the first step you will prepare an amount of the master mix sufficient to 6 samples of DNA by adding the special reagents for the experiment in the master mix tube.

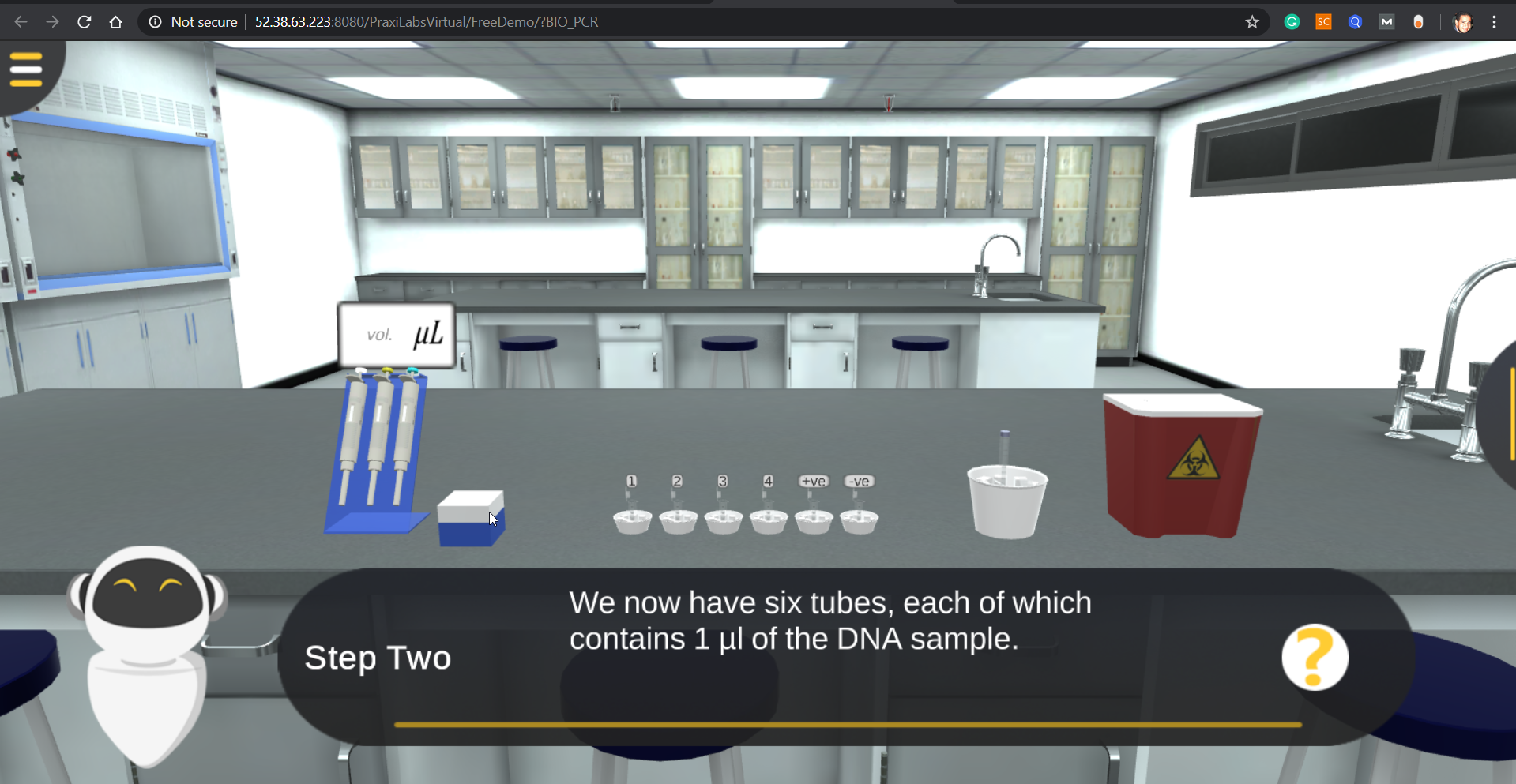
Then, the laboratory moves to the DNA extraction room, where you will add 49 μl of the master mix that you prepared in the previous step to 1 μl of each DNA sample.
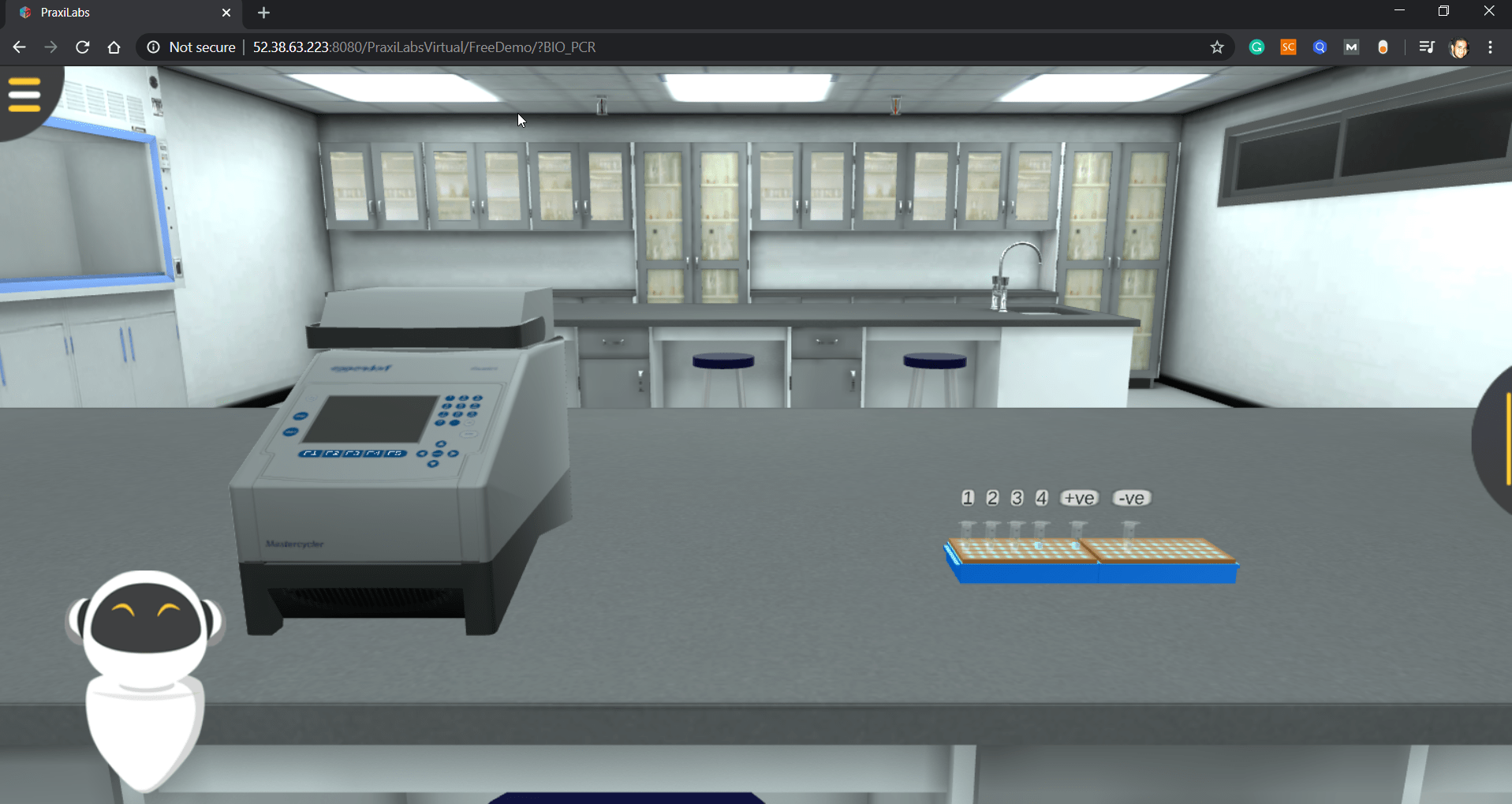
Then you will move to the PCR device. At this stage, we will place the Eppendorf tubes in the thermal cycler and then adjust the device settings for three stages until the separation process is completed.
Other Applications of PCR Analysis:
Because of this great sensitivity, PCR has found popularity in a wide range of applications. Molecular biologists use PCR in gene cloning and DNA sequencing. Forensic scientists use PCR to connect blood, saliva, or tissue left at the scene of a crime to a suspect or victim. Clinical geneticists use PCR to determine whether or not potential parents might carry a genetic disease that could be passed along to their children.
Thus, the PCR analysis experiment is one of the most important experiments that students of biology and medicine should understand, and therefore PraxiLabs provides it as part of its initiative to support practical colleges during the period of study interruption due to the current circumstances.
PraxiLabs Virtual Labs include a range of 3D science experiments in physics, chemistry and biology experiments
 PraxiLabs A virtual world of science
PraxiLabs A virtual world of science





