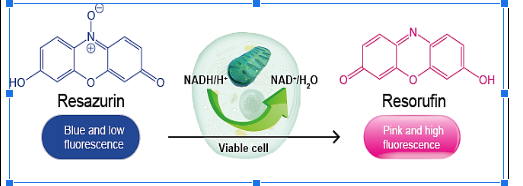
In Vitro Cell Viability by the Alamar Blue Assay
Biology | Toxicology | Biochemistry | Pharmacology






2.5M+
Active Users Worldwide
80%
Improved Learning Retention
60%
Reduction in Laboratory Costs
In Vitro Colorimetric Analysis of Cell Viability by Alamar Blue Assay
By the end of alamar blue test experiment, students will: