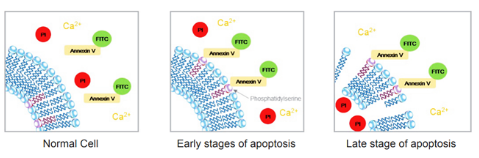
In-Vitro Annexin V Assay Binding/Propidium Iodide Uptake
Biology | Toxicology | Biochemistry | Pharmacology






2.5M+
Active Users Worldwide
80%
Improved Learning Retention
60%
Reduction in Laboratory Costs
The annexin v assay experiment aims at detecting and quantifying apoptotic and necrotic cells through Annexin V assay binding and Propidium Iodide (PI) uptake using a fluorescent microscope.
In Vitro Annexin V Binding/Propidium Iodide Uptake Assay using Fluorescence Microscope.
By the end of Annexin V Assay experiment, the post-graduate student will be able to:
In the Annexin V assay: