In-Vitro Bromodeoxyuridine BrdU Assay
Biology | Toxicology | Biochemistry | Pharmacology






2.5M+
Active Users Worldwide
80%
Improved Learning Retention
60%
Reduction in Laboratory Costs
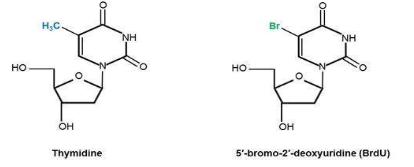
The BrdU assay experiment aims at visualizing the Bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU assay) incorporation as a thymidine analogue into nuclear DNA in order to detect DNA synthesis in vitro using antibody probes and a fluorescent microscope.
In Vitro Immunofluorescence Assay for detection of incorporated BrdU during DNA replication using BrdU cell proliferation assay.
Successfully handle the required instruments and consumables needed in the brdu assay experiment according to brdu assay protocol.