Cloning Blue and White Screening
Biology | Biochemistry | Genetics | Microbiology





2.5M+
Active Users Worldwide
80%
Improved Learning Retention
60%
Reduction in Laboratory Costs
To perform blue and white screening of plated bacteria, and to calculate the transformation efficiency.
Blue and white screening
To perform blue and white screening.
The recombinant molecule which contains the DNA fragment of interest. (‘expt/comp’)
Uncut pUC19, prepared as a control. (‘uncut pUC19/comp’)
Sterile water, also prepared as a control. (‘no DNA/comp’)
Then, the spread-plate technique is used to plate the culture of the transformed bacteria onto a medium containing Ampicillin, X-Gal, and IPTG (isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactopyranoside).
E. coli JM101 plated cannot survive and grow in the presence of the antibiotic ampicillin.
The pUC19 plasmid carries the ‘Ampr’ gene that codes for resistance to the antibiotic ampicillin.
Therefore, any cell transformed with the pUC19 plasmid will be converted to the ampicillin-resistant phenotype (Ampr) and will be able to grow in the presence of ampicillin. Thus, Ampicillin is used for the selection of successful transformants.
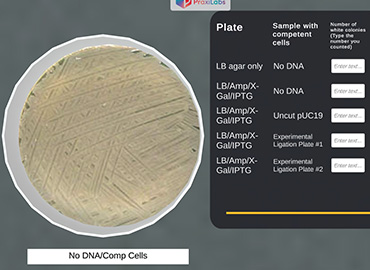
The control plate ‘only LB agar’ plated with ‘no DNA/comp’ shows white colonies ‘lawn’ since the JM101 can grow in the absence of ampicillin.
The control plate ‘LB/Amp/X-Gal/IPTG’ plated with ‘no DNA/comp’ should show no growth of bacteria.
Colonies appear in two colors, blue or white. Blue–white screening explained by the presence or absence of a functional lacZ gene encoding β-galactosidase.
Blue colonies are the result of hydrolysis of X-Gal present in the medium by β-galactosidase.
β-galactosidase is produced only in the presence of a functional lacZ gene. E. coli JM101 lacks a functional lacZ gene.
The control plate ‘only LB agar’ plated with ‘no DNA/comp’ shows white colonies due to the absence of the lacZ gene.
When pUC19 plasmid (not ligated to yeast DNA fragment) is inserted into the JM101, a functional lacZ gene is formed by α-complementation.
The plate ‘LB/Amp/X-Gal/IPTG’ is plated with ‘uncut pUC19/comp’ (control plate).
The plate ‘LB/Amp/X-Gal/IPTG’ is plated with ‘expt/comp’ sample but there was a failure of ligation of pUC19 to the recombinant molecule (experimental plate).
When pUC19 containing the recombinant molecule is inserted into the JM101, a functional lacZ gene is not created. β-galactosidase will not be produced, and colonies will appear white.
X-Gal/IPTG are thus used to select successful ligation of yeast DNA fragment of interest to the pUC19 plasmid through blue white selection in cloning. This occurs in the plate ‘LB/Amp/X-Gal/IPTG’ plated with ‘expt/comp’ sample.
To sum up, the colonies formed by non-recombinant cells appear blue while the recombinant ones appear white. The calculation of the efficiency of transformation can be done using blue/white screening.
Successful cloning shows transformation efficiencies for E. coli at least in the range of 106 transformants per µg of plasmid DNA.
You will comment on each plate—both control and experimental—and fill in the table provided.
Transformation efficiency = number of colonies on plate / concentration of DNA plated (ng) * 10000 = -------- ng/µg.




