




2.5M+
Active Users Worldwide
80%
Improved Learning Retention
60%
Reduction in Laboratory Costs
The Gram Stain is a very important preliminary step in the initial characterization and classification of bacteria.
It is also a key procedure in the identification of bacteria based on staining characteristics, enabling the bacteria to be examined using a light microscope.
The bacteria present in an unstained smear are invisible when viewed using a light microscope. Once stained, the morphology and arrangement of the bacteria may be observed as well.
Furthermore, it is also an important step in the screening of infectious agents in clinical specimens such as direct smears from a patient.
The Four Basic Steps of the Gram Staining Experiment are: 1 - Application of the primary stain Crystal Violet (CV) to a heat-fixed smear of bacterial culture. CV dissociates in aqueous solutions into CV+ and Cl – ions. These two ions then penetrate through the cell wall and cell membrane of both Gram-positive and Gram-negative cells. The CV+ ions later interact with negatively charged bacterial components and stain the bacterial cells purple. 2 - Addition of Gram’s Iodine. Iodine (I – or I3 –) acts as a mordant and as a trapping agent. A mordant is a substance that increases the affinity of the cell wall for a stain by binding to the primary stain, thus forming an insoluble complex that gets trapped in the cell wall. In the Gram Stain reaction, the crystal violet and iodine form an insoluble complex (CV-I) which serves to turn the smear a dark purple color. At this stage, all cells will turn purple. 3 - Decolorization with 95% ethyl alcohol. Alcohol or acetone dissolves the lipid outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria, thus leaving the peptidoglycan layer exposed and increasing the porosity of the cell wall. The CV-I complex is then washed away from the thin peptidoglycan layer, leaving Gram-negative bacteria colorless. On the other hand, alcohol has a dehydrating effect on the cell walls of Gram-positive bacteria which causes the pores of the cell wall to shrink. The CV-I complex gets tightly bound into the multi-layered, highly cross-linked Gram-positive cell wall thus staining the cells purple. The decolorization step must be performed carefully; otherwise, over-decolorization may occur. This step is critical and must be timed correctly otherwise the crystal violet stain will be removed from the Gram-positive cells. If the decolorizing agent is applied to the cell for too long time, the Gram-positive organisms are to appear Gram-negative. Under-decolorization occurs when the alcohol is not left on long enough to wash out the CV-I complex from the Gram-negative cells, resulting in Gram-negative bacteria to appear Gram-positive. 4 - Counterstain with Carbol fuchsin The decolorized Gram-negative cells can be rendered visible with a suitable counterstain, which is usually positively charged, which stains them pink. The pink color which adheres to the Gram positive bacteria is masked by the purple of the crystal violet. The Gram stain procedure enables bacteria to retain the color of the stains, based on the differences in the chemical and physical properties of the cell wall. 1. Gram-positive bacteria: Stain dark purple due to retaining the primary dye called Crystal Violet in the cell wall. 2. Gram-negative bacteria: Stain red or pink due to retaining the counter staining dye called carbol fuchsin.
To become proficient at performing the gram stain consistently and accurately in the gram stain virtual lab.
Staining is an auxiliary technique used in microscopic techniques to enhance the clarity of the microscopic image.
Stains and dyes are widely used in the scientific field to highlight the structure of the biological specimens, cells, tissues, etc through various staining techniques in microbiology.
The most widely used staining procedure in microbiology is the Gram stain, discovered by the Danish scientist and physician Hans Christian Joachim Gram in 1884.
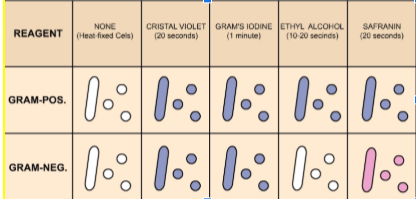
The procedure is based on the ability of microorganisms to retain the color of the stains used during the gram stain reaction.
Gram-negative bacteria are decolorized by the alcohol, losing the color of the primary stain, purple.
Gram-positive bacteria are not decolorized by alcohol and will remain purple.
After the decolorization step, a counterstain is used to impart a pink color to the decolorized gram-negative organisms in the gram staining simulation.
The key step to their differentiation is the decolorization, which can be practiced using a gram stain simulator or virtual gram stain lab.
During the crystal violet-iodine step, the bound molecules within the peptidoglycan of the Gram + cell wall and within the membrane are held tightly
The ethyl-alcohol causes the peptidoglycan molecules (arranged in a latticework) to shrink, thereby holding the crystal violet iodine even tighter.
In the gram – cell, the outer lipopolysaccharide layer of the wall is dissolved by the decolorizer agents, and because the peptidoglycan layer is so thin in that group of bacteria, the crystal violet is leached out of the wall in the gram stain simulation.
The conclusion for gram staining experiment demonstrates the effectiveness of this technique in differentiating bacterial cell wall structures, which can also be explored in the virtual gram staining lab or gram staining virtual lab environment.




