In-Vitro Cytokinesis-Block Micronucleus Assay (CBMN Assay)
Biology | Toxicology | Biochemistry | Proteomics | Pharmacology






2.5M+
Active Users Worldwide
80%
Improved Learning Retention
60%
Reduction in Laboratory Costs
The in vitro mammalian cell micronucleus test aims at detecting the (Chromosomal damage) damage of chromosomes, both chromosome loss and chromosome breakage, to evaluate the induction of genotoxic effects of nanoparticles and nanomaterials using the light microscope.
In Vitro Cytokinesis-Block Micronucleus Assay using Microscopy
By the end of this micronucleus test, the postgraduate student will be able to:
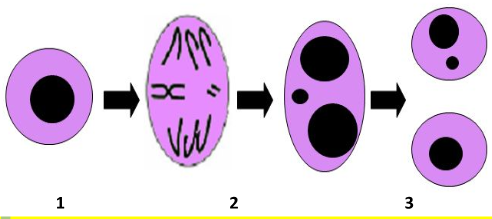
Figure 1: Cell starts its cell cycle and replication of its genetic materials (1), under various genotoxic stresses, (Chromosomal damage occurs during replication) chromosomes are damaged during replication (2), the damaged fragments are not segregated by spindles and form micronuclei (3), and Micronuclei are separated into divided cells (4)




