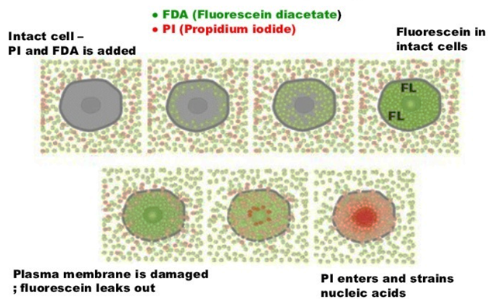
Fluorescein Diacetate Assay (In-Vitro (FDA/PI) Staining)
Biology | Toxicology | Biochemistry | Proteomics | Pharmacology






2.5M+
Active Users Worldwide
80%
Improved Learning Retention
60%
Reduction in Laboratory Costs
The fluorescein diacetate assay experiment aims at calculating the viability percent of cultured adherent cells after excitation of free fluorescein cleaved by esterase enzymes in live cells using a fluorescent microscope.
In Vitro Fluorescein Diacetate/Propidium Iodide (FDA/PI) Staining Assay using fluorescence microscope.
By the end of propidium iodide assay experiment, the postgraduate student will be able to:
Cytotoxicity is the quality of being toxic to cells. Cytotoxicity assays are widely used by the pharmaceutical industry to screen for cytotoxicity in compound libraries.
Researchers, as in Nanotechnology, can either look for cytotoxic nano-based materials, if they are interested in developing a nanomedicine that targets rapidly dividing cancer cells, for instance, or they can screen "hits" from initial high-throughput nanoparticle screens for unwanted cytotoxic effects before investing in their development as a nanomedicine.
Assessing cell membrane integrity is one of the most common ways to measure cell viability and cytotoxic effects. Compounds that have cytotoxic effects often compromise cell membrane integrity.
Vital dyes, such as trypan blue or propidium iodide, are normally excluded from the inside of healthy cells; however, if the cell membrane has been compromised, they freely cross the membrane and stain intracellular components.
Alternatively, membrane integrity can be assessed by monitoring the passage of substances that are normally sequestered inside cells to the outside.
Protease biomarkers have been identified that allow researchers to measure relative numbers of live and dead cells within the same cell population.
The live-cell protease is only active in cells that have a healthy cell membrane and loses activity once the cell is compromised and the protease is exposed to the external environment.
The dead-cell protease cannot cross the cell membrane and can only be measured in culture media after cells have lost their membrane integrity.
Cytotoxicity can also be monitored by measuring the reducing potential of the cells using a colourimetric reaction, or using ATP content as a marker of viability.
Such ATP-based assays include bioluminescent assays in which ATP is the limiting reagent for the luciferase reaction.
A label-free approach to follow the cytotoxic response of adherent animal cells in real-time provides the kinetics of the cytotoxic response rather than just a snapshot like many colourimetric endpoint assays.