In-Vitro Neutral Red Uptake Assay
Biology | Toxicology | Biochemistry | Proteomics | Pharmacology






2.5M+
Active Users Worldwide
80%
Improved Learning Retention
60%
Reduction in Laboratory Costs
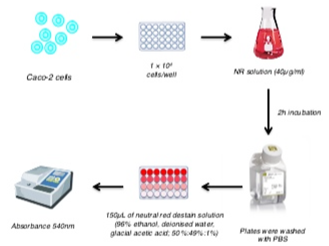
The neutral red uptake assay experiment aims at quantifying the amount of absorbed supravital dye Neutral Red (NR) in lysosomes of viable cells using a microplate spectrophotometer (Microplate Reader).
In Vitro Neutral Red uptake assay using microplate spectrophotometer.
By the end of neutral red uptake test experiment, the postgraduate student will be able to: