




2.5M+
Active Users Worldwide
80%
Improved Learning Retention
60%
Reduction in Laboratory Costs
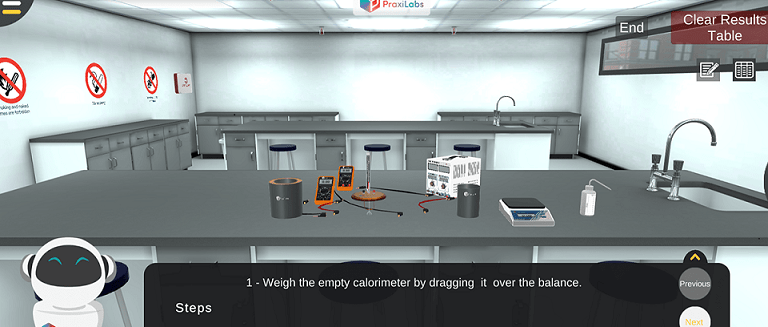
1- Determine the value of the mechanical equivalent of heat coefficient through Joule's experiment.
2- Determine the value of coil resistance in the calorimeter virtual lab.
Conversion of electrical energy into heat energy in Joule heating simulation.
By the end of Joule’s experiment, the student should be able to:
In Joule's experiment, the following steps is implemented:




