




2.5M+
Active Users Worldwide
80%
Improved Learning Retention
60%
Reduction in Laboratory Costs
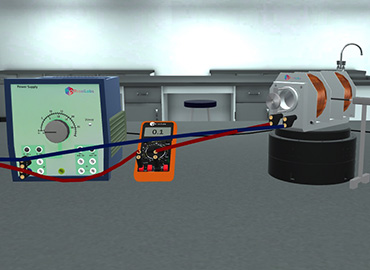
Normal Zeeman splitting of spectral lines.
By the end of Zeeman effect simulation, the student should be able to:
1D2 (J = 2, S = 0) → 1P1 (J = 1, S = 0)
ΔMJ = +1; ΔMJ = 0; ΔMJ = –1
are taken into account. In this case, therefore, there are a total of nine permitted transitions, only three of which ever have the same energy and hence the same wavelength. Therefore, only three lines will be visible.




