Last Updated on November 16, 2022 by Sherouk Badr Shehata
The PCR test is a method of amplifying specific DNA sequences using taq polymerase. This technique was first developed in the 1980s and has since revolutionized biology testing. Prior to PCR, only small amounts of DNA could be isolated and analyzed from samples. However, PCR allows for the amplification of minute amounts of DNA, making it possible to obtain accurate results from even trace amounts of genetic material.
Taq polymerase is a key enzyme in the famous PCR (polymerase chain reaction), a powerful technique used to amplify DNA. Taq polymerase is able to withstand the high temperatures required to denature DNA, and can then efficiently copy the template DNA strand. This makes it an essential tool for PCR-based applications such as DNA sequencing, forensics, and genetic engineering.
Taq polymerase is used in research to study the function of genes and to develop new diagnostic tests and treatments for diseases. Its discovery and its role in PCR has had a profound impact on science and society, and this enzyme continues to be an essential tool in modern biotechnology.
Additionally, taq polymerase has an important role in ensuring the fidelity of DNA replication. Therefore, it is a vital component in PCR testing and plays a crucial role in ensuring accurate and reliable results. Taq polymerase is also relatively inexpensive and easy to obtain, making it a popular choice for many laboratories.
Table of Contents
Taq Polymerase: What Is This?
Taq polymerase is a thermostable enzyme that is used in PCR (polymerase chain reaction). This enzyme is able to hold out against high temperatures, making it ideal for use in PCR. Taq polymerase has an important role in PCR, as it is responsible for amplifying the DNA template. This enzyme is crucial for PCR applications such as DNA sequencing, forensics, and diagnostics.
Taq polymerase is also used in other molecular biology techniques such as qPCR (quantitative PCR) and RT-PCR (reverse transcription PCR). Taq polymerase is a key enzyme in these techniques, as it allows for the amplification of DNA or RNA templates. Taq polymerase is produced by the bacterium Thermus aquaticus, which is found in hot springs. This enzyme was first isolated in 1976 and has since been used extensively in PCR applications.
Taq Polymerase and PCR: The History Behind!
Taq polymerase is a thermostable DNA polymerase named after the thermophilic bacterium Thermus aquaticus from which it was originally isolated by Thomas D. Brock in 1965. PCR is a technique that amplifies specific segments of DNA, and taq polymerase is essential for this process. In taq polymerase-mediated PCR, short stretches of DNA called primers are used to initiate the synthesis of new DNA strands. Taq polymerase then extends these strands, resulting in the amplification of the target sequence.
This enzyme is notable for its ability to face extremely high temperatures, making it an important tool in the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method of amplifying DNA. PCR is a technique used to amplify specific regions of DNA in order to allow for closer study and analysis. Taq polymerase is able to endure the high temperatures required for PCR due to its origin from thermophilic bacteria, which are able to live in hot environments.
PCR was first developed in the early 1980s, and taq polymerase played a key role in its success. Taq polymerase is a thermostable enzyme, meaning that it is stable at high temperatures. This is important for PCR because the process involves repeatedly heating and cooling the DNA sample to achieve the desired amplification. Thanks to these properties, taq polymerase quickly became one of the most important tools in molecular biology and genetics as mentioned previously.
Why Taq Polymerase Is Used in PCR?
The PCR process involves heating and cooling cycles to separate the double-stranded DNA template, denature the DNA strands, anneal the primers to the template, and extend the primers using taq polymerase. Taq polymerase is active over a wide range of temperatures, from 40-75°C. The optimum temperature for taq polymerase activity is around 72°C. Taq polymerase can also endure the high temperatures used in the PCR process, up to 95°C.
Taq polymerase has a number of features that make it ideal for use in PCR. Firstly, taq polymerase has a high tolerance for mismatches between the primer and template DNA. This is important because PCR amplifies DNA from very small quantities of starting material, and the primers may not perfectly match the template DNA. Secondly, taq polymerase has a proofreading activity that enables it to error-free amplify DNA templates. This is important because PCR amplifies DNA to extremely high levels, and any errors in the PCR product can lead to problems downstream.
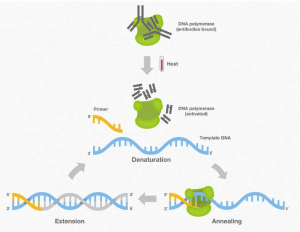
Taq polymerase is an essential enzyme for PCR and has been extensively studied. Taq polymerase is a thermostable enzyme that can withstand the high temperatures used in the PCR process. Taq polymerase has a high tolerance for mismatches between the primer and template DNA, and a proofreading activity that enables it to error-free amplify DNA templates. Taq polymerase is an essential enzyme for PCR and its structure and function are well-understood.
In PCR Tests: What Is the Function of Taq Polymerase?
Taq polymerase is a thermostable DNA polymerase that is routinely used in PCR. It catalyzes the synthesis of new DNA strands by adding nucleotides to the 3’ end of a template strand. This process is known as DNA replication. In order for Taq polymerase to accurately replicate the template strand, it must first bind to the template strand. Once bound, Taq polymerase uses its own thermal stability to elongate the DNA strand by adding nucleotides.
The high fidelity of taq polymerase results in very few mistakes being made during DNA replication. This is important because PCR is often used to amplify specific sequences of DNA. If Taq polymerase made a lot of mistakes, the amplified DNA would not be accurate and could lead to false results.
Taq polymerase copes with high temperatures. This is important because PCR requires the repeated heating and cooling of the reaction mixture. If Taq polymerase was not stable at high temperatures, it would be denatured and would no longer function properly. Overall, Taq polymerase is essential for PCR tests. Its high fidelity and thermal stability make it ideal for this purpose. without Taq polymerase, PCR would not be possible.
Using Taq Polymerase– The Protocol to Be Followed!
Since it remains active at temperatures that denature double-stranded DNA, taq polymerase is frequently used in PCR, thus allowing for the amplification of specific regions of DNA (or cDNA). It synthesizes DNA using the template strand as a primer to extend the new complementary strand.
The enzyme has 5′-3′ exonuclease activity, but lacks significant 3′-5′ exonuclease activity, making it unsuitable for use in long-range PCR or for applications that require proofreading activity. Despite these limitations, Taq polymerase has been used effectively in a wide variety of PCR applications.
Taq polymerase is a member of the enzymes family, which includes other thermostable DNA polymerases such as Deep Vent (exo-) and Vent (exo-). All three of these enzymes are derived from Thermococcus species. It was the first thermostable DNA polymerase to be purified and characterized.
The optimal reaction conditions for taq polymerase-catalyzed PCR depend on a number of factors, including the template DNA, the primers, and the dNTPs. In general, however, reactions are carried out at 94-95°C for denaturation, 50-60°C for annealing, and 72°C for extension. Magnesium ion is often used as a cofactor in PCR reactions, and the optimum concentration of Mg2+ can vary depending on the reaction conditions.
PCR reactions catalyzed by Taq polymerase are typically performed in a volume of 50-200 μL. The following components are typically added to the reaction mixture:
- Template DNA
- Forward and reverse primers (10-50 pmoles each)
- dNTPs (250-500 μM each)
- 10X PCR buffer (100 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.3 at 25°C, 500 mM KCl, 15 mM MgCl2)
- Taq polymerase (5-10 units/reaction)
The specific composition of the reaction mixture will vary depending on the application. For example, if amplification of a long sequence is desired, more template DNA and primer may be used. In addition, different buffers or enzyme formulations may be used depending on the specifics of the reaction.
The protocol for using taq polymerase in PCR is as follows:
- Denature the template DNA by heating it to 94-96°C for 2-5 minutes.
- Add the Taq polymerase to the reaction mixture and then cool the mixture to 50-60°C for 1 minute.
- Add the primer to the reaction mixture and then cool the mixture to 50-60°C for 1 minute.
- Extend the primer by heating the mixture to 72°C for 1-2 minutes.
- Repeat steps 2-4 for each cycle of amplification desired.
- Final extension is carried out by heating the mixture to 72°C for 7 minutes.
- Hold the reaction at 4°C until ready to use.
- Taq polymerase can be stored at -20°C for long-term storage.
Taq polymerase has also been used in other applications beyond PCR, including DNA sequencing, site-directed mutagenesis, and cDNA synthesis.
The Use of Taq Polymerase in Forensics
The use of Taq polymerase in forensics was first reported in 1985, just a few years after the discovery of PCR. In the early days of forensic DNA analysis, PCR was used to amplify whole genome sequences. However, this method was not very sensitive and could not detect very small amounts of DNA. Taq polymerase allowed for the development of more sensitive methods of DNA amplification, such as the STR (short tandem repeat) method. The STR method is now the most commonly used method of DNA analysis in forensics. It can detect very small amounts of DNA and is very sensitive.
Taq polymerase has also been used in other areas of forensic science, such as the analysis of fingerprints. It can be used to amplify the DNA from a fingerprint, which can then be analyzed for matches with other fingerprints. It is often used to amplify faint or degraded DNA samples. This makes it possible to obtain usable information from samples that would otherwise be unusable.

One advantage of using taq polymerase in forensics is that it is relatively easy to obtain and use. This enzyme is commercially available and can be purchased from various scientific supply companies. It can also be used to amplify mitochondrial DNA, which can be helpful in cases where nuclear DNA is unavailable or degraded. It is also stable and can be stored at room temperature for long periods of time.
However, there are some disadvantages to using this technique in forensics. One disadvantage is that this enzyme can sometimes amplify DNA contaminants present in a sample. This can lead to false positive results or incorrect information being obtained from a sample. Additionally, it is not always effective at amplifying all types of DNA, including certain types of degraded DNA.
Despite the disadvantages, taq polymerase remains a valuable tool for forensic scientists. This enzyme can be used to obtain usable information from samples that would otherwise be unusable. It is relatively easy to obtain and use, making it a convenient tool for forensic scientists.
Taq polymerase has had a major impact on forensic science and it has allowed for the development of more sensitive methods of DNA amplification and analysis. These methods have helped to solve many crimes and have led to the conviction of many criminals.
Research and Taq Polymerase: A Copious Number of Applications!
Taq polymerase is a versatile enzyme that has many uses in research. It is commonly used in PCR, DNA sequencing, mutagenesis, and gene expression studies. PCR is commonly used in diagnostic applications such as detecting disease-causing mutations or identifying pathogens. It is also used in DNA sequencing reactions. In these reactions, Taq is used to create copies of a DNA template that are then sequenced. This allows for the determination of the order of nucleotides in a particular DNA sequence.
Mutagenesis experiments also use taq polymerase. In these experiments, it is used to introduce mutations into a DNA sequence. This can be done by either randomly incorporating nucleotides into the DNA template or by targeted mutagenesis. Targeted mutagenesis is a technique that allows for the introduction of specific mutations into a DNA sequence. This can be useful in studies investigating the effects of specific mutations on gene function.
Lastly, taq polymerase is also used in gene expression studies. Gene expression is the process by which a gene’s DNA sequence is used to produce a functional protein. It can be used to create multiple copies of a particular DNA sequence, which can then be used to study gene expression. This can be useful in understanding how genes are regulated and how they contribute to the function of a cell or organism. Nevertheless, taq polymerase is an essential tool in many areas of research and will continue to be used in new and innovative ways.
Taq Polymerase and the Future
What will the future of taq polymerase hold? Only time will tell, but we can be sure that this enzyme will continue to play an important role in the field of molecular biology. As our understanding of DNA grows, so too will the importance of taq polymerase in helping us to study and manipulate this molecule. With its ability to quickly and accurately copy large stretches of DNA, taq will continue to be an essential tool for scientists around the world.
Join PraxiLabs for FREE to know more about the experiments and applications of this enzyme!
